Eve Online, the space-based videogame with over half a million active players, has been forced offline for more than 12 hours due to a series of cyber attacks against a cluster of its servers located in London. According to the Eve Online Status Twitter account, the first signs of trouble were seen at around 8pm on Thursday, 21 August, and by 11pm the Icelandic-based CCP Games which develops the game had confirmed the problem was due to a series of distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. DDoS attacks are a common tool used by criminals to flood servers with traffic in order to knock them offline and unavailable to anyone trying to access them. Some had apparently linked the offline status of the game to the recent activity of the Bardarbunga volcano in Iceland which is on the verge of erupting, however CCP Games explicitly ruled this out. The problem is affecting the Tranquility server cluster, which all Eve Online players connect to in order to play the game. This cluster of servers is based in London. Even the Eve Online wiki is inaccessible as it too is seemingly hosted on the Tranquility server. An update from CCP Games on Twitter at 8am on Friday, 22 August, simply saying: “Tranquility is currently under heavy load again” and pointing player to a forum thread. However this thread also appears to be offline at the time of publication. DDoS attacks are often used by unscrupulous companies in order to knock rivals offline for a sustained period of time, with many cyber-criminals renting out DDoS services for as little as £5-an-hour. Eve Online is a massively multiplayer online game set in the fictional world of New Eden where players pilot customisable spaceships through a galaxy of over 7,500 star systems. The game is also unique in that its developers create the structure of New Eden but then handed over control of what happens in the game to the players. The rest is a virtual world where corporations and alliances hold huge power and where huge battles can cost the equivalent of over $300,000 in real world money. Source: http://www.ibtimes.co.uk/eve-online-servers-knocked-offline-due-ddos-attacks-1462180
Continue Reading:
Eve Online Servers Knocked Offline Due to DDoS Attacks


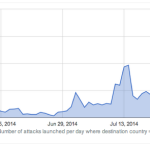 As conflict between Israel and the Palestinian militant Islamist organisation Hamas escalates, new research has revealed the impact politics has had on cyberattack trends. Tension between countries and changing political landscapes can now often be linked to cybercrime campaigns worldwide. From constant spats between the US and China to increased targeting of Syrian and Thai targets during political unrest, digital weaponry is now a key tool for groups to broadcast their own political messages, spy on governmental agencies and steal valuable data. In a new report released by Arbor Networks, anonymized traffic and DDoS attack data from over 290 ISPs that have deployed Arbor’s Peakflow SP product — collated and analyzed as part of Arbor’s ATLAS initiative — it appears that DDoS attacks are rising in number and volume as a result of the Israel-Hamas conflict. The graph below depicts the number of reported DDoS attacks initiated against Israel daily over the 1 June to 3 August period this year: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are used to flood a website or service with traffic to the point systems cannot cope, denying other users access to the website. Arbor detected a rise in the number of DDoS attacks targeting Israel in the first week of July, going from an average of 30 attacks per day to an average of 150 attacks initiated per day in July — peaking at 429 attacks on July 21st. Linking these cyberattacks to political situations, 30 June is when Israel publicly attributed the deaths of three kidnapped Israeli teenagers to Hamas, and on 7 July, “Operation Protective Edge” was launched by the country. As the political conflict raged on, so did the frequency of DDoS attacks until a drop occurred on 28 July lasting through 2 August. Arbor says the drop in attacks roughly correlates with cease fire talks which began 27 July. From 28 July through 2 August, there were 192 attacks recorded in total. On 3 August, the number of DDoS attacks rose sharply, with 268 attacks in total. In addition to the number of DDoS attacks over these time periods, the security researchers also noticed an increase in the peak size of these attacks. In the graph below, we can see that in June, no attacks exceeded 12Gbps. In July, seven DDoS attacks exceeded this size, with the largest peaking at 22.56Gbps on 12 July. When cease-fire talks fell apart on 3 August, the largest DDoS attack was recorded at a size of 29Gbps. The duration of DDoS attacks has also increased. In June, the average duration was 20 minutes — with a peak duration of 24 hours — and in July, the average duration was 1 hour 39 minutes. “As the intensity of the Israeli-Hamas conflict has increased, so has the number, size and duration of the DDoS attacks targeting Israel,” the researchers say. “Additionally, it even appears as if the attackers have made an effort to adhere to the “real world” calls for a cease-fire, resuming their attacks when the cease fire fell through.” Source: http://www.zdnet.com/israel-hamas-conflict-sparks-surge-in-ddos-attacks-7000032375/#ftag=RSS14dc6a9
As conflict between Israel and the Palestinian militant Islamist organisation Hamas escalates, new research has revealed the impact politics has had on cyberattack trends. Tension between countries and changing political landscapes can now often be linked to cybercrime campaigns worldwide. From constant spats between the US and China to increased targeting of Syrian and Thai targets during political unrest, digital weaponry is now a key tool for groups to broadcast their own political messages, spy on governmental agencies and steal valuable data. In a new report released by Arbor Networks, anonymized traffic and DDoS attack data from over 290 ISPs that have deployed Arbor’s Peakflow SP product — collated and analyzed as part of Arbor’s ATLAS initiative — it appears that DDoS attacks are rising in number and volume as a result of the Israel-Hamas conflict. The graph below depicts the number of reported DDoS attacks initiated against Israel daily over the 1 June to 3 August period this year: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are used to flood a website or service with traffic to the point systems cannot cope, denying other users access to the website. Arbor detected a rise in the number of DDoS attacks targeting Israel in the first week of July, going from an average of 30 attacks per day to an average of 150 attacks initiated per day in July — peaking at 429 attacks on July 21st. Linking these cyberattacks to political situations, 30 June is when Israel publicly attributed the deaths of three kidnapped Israeli teenagers to Hamas, and on 7 July, “Operation Protective Edge” was launched by the country. As the political conflict raged on, so did the frequency of DDoS attacks until a drop occurred on 28 July lasting through 2 August. Arbor says the drop in attacks roughly correlates with cease fire talks which began 27 July. From 28 July through 2 August, there were 192 attacks recorded in total. On 3 August, the number of DDoS attacks rose sharply, with 268 attacks in total. In addition to the number of DDoS attacks over these time periods, the security researchers also noticed an increase in the peak size of these attacks. In the graph below, we can see that in June, no attacks exceeded 12Gbps. In July, seven DDoS attacks exceeded this size, with the largest peaking at 22.56Gbps on 12 July. When cease-fire talks fell apart on 3 August, the largest DDoS attack was recorded at a size of 29Gbps. The duration of DDoS attacks has also increased. In June, the average duration was 20 minutes — with a peak duration of 24 hours — and in July, the average duration was 1 hour 39 minutes. “As the intensity of the Israeli-Hamas conflict has increased, so has the number, size and duration of the DDoS attacks targeting Israel,” the researchers say. “Additionally, it even appears as if the attackers have made an effort to adhere to the “real world” calls for a cease-fire, resuming their attacks when the cease fire fell through.” Source: http://www.zdnet.com/israel-hamas-conflict-sparks-surge-in-ddos-attacks-7000032375/#ftag=RSS14dc6a9