The agency is working on a multimillion dollar effort to protect the country’s most critical systems from distributed denial of service attacks, which are among the simplest digital assaults to carry out and the toughest to fight. MARCH 8, 2017 —In late October, in Surprise, Ariz., more than 100 phone calls bombarded the police department’s emergency dispatch line. Calls also overwhelmed the nearby city of Peoria’s 911 system and departments across California and Texas. But each time a dispatcher picked up, no one was on the line – and there was no emergency. The Arizona district attorney’s office says the calls clogging 911 lines resulted from a digital prank, which triggered a distributed denial of service, or DDoS, attack on critical emergency communication systems. The prosecutor’s office tracked the torrent of calls to 18-year-old hacker Meetkumar Hiteshbhai Desai. Now, he’s facing four counts of felony computer tampering. While Mr. Desai said he didn’t intend to cause any harm, according to the Maricopa County Sheriff’s Office, he did surface a potentially devastating glitch in smartphone software that could exact damage on any number of sensitive and critical targets. Whenever anyone clicked a certain link on his webpage via a mobile device, their phone automatically dialed 911. While this kind of DDoS targeting 911 systems is unprecedented, it’s exactly the type of attack that national law enforcement officials have been concerned about for years. In fact, the Homeland Security Department (DHS) has been working on technology to protect 911 centers from DDoS and telephone-based, or TDoS, attacks for three years. The Arizona incident proved someone can “cause a large number of phones or a large number of computers or a large number of whatever connected device to start generating these calls,” says Dan Massey, program manager in the cybersecurity division of the DHS Science and Technology Directorate. “It went from how much damage can I do from my phone” to a situation where, with just a handful of people, “if all of our phones started calling some victim, whether that’s 911 or a bank or a hospital, that can get very fast and very big.” DDoS attacks are both among the simplest forms of cyberattacks to carry out and the most difficult to defend against. They are designed to direct an overwhelming amount of digital traffic – whether from robocalls or web traffic – at targets to overwhelm them so they can’t handle legitimate business. Writ large, there has been an exponential increase in the intensity and frequency of DDoS attacks over the past six months and critical infrastructure components are possible future targets, according to DHS. For a sense of the scale of today’s DDoS attacks, compare the 100 megabits per second Internet speed at a typical company to the more than 1 million megabits (1 terabit) per second speed of a DDoS attack against Web hosting company Dyn in October. The attack, which drew power from insecure webcams and other internet-connected devices, knocked out widely used online services like Netflix, Twitter, and Spotify for hours. Such massive web DDoS assaults may also become a problem for 911, as the country moves toward a next generation 911 system that uses mapping services to locate callers and can support voice, text, data, and video communication. “What you’re seeing is a convergence of the traditional internet with the phone system and next generation 911 is a great example of that,” says Massey. “DDoS attacks and/or TDoS attacks kind of blend together a little bit there.” To help combat the problem, the department has given out $14 million in grants for DDoS prevention studies, including phone-based attacks. Some of that funding is piloting initiatives to stop phone-based attacks at 911 centers in Miami/Dade County and the City of Houston, as well as at a large bank that the department wouldn’t identify. So far, DHS efforts have yielded, among other things, a DDoS early warning system to flag organizations that an attack may be coming, and alerting them to adjust internet network settings to defend against an onslaught of traffic. Additionally, DHS-funded research from tech firm SecureLogix produced a prototype that can thwart phony telephone calls sent to a 911 system or other critical phone operation. The model attempts to detect bogus calls by monitoring for clues that indicate an incoming call is fake. “As we have seen, it is simple to flood a 911 center, enterprise contact center, hospital, or other critical voice system with TDoS calls,” says Mark Collier, SecureLogix chief technology officer. “The research is essential to get ahead” because the assailants “are generating more attacks, the attacks are more sophisticated, and the magnitude of the attacks is increasing. “ To be sure, the race to keep digital adversaries out of the country’s 911 system faces obstacles, some of which are outside the jurisdiction of Homeland Security and dispatch centers. The DHS DDoS defense program is “a good start,” but one “challenge in defending certain types of critical infrastructure is the fact that emergency services like 911 must serve anyone – immediately,” per Federal Communications Commission rules, “due to their life saving nature,” said Mordechai Guri, research and development head at Israel’s Ben-Gurion University Cyber-Security Research Center. “The approach of blocking the DDoS originators must be backed by a change in the laws and regulations.” Before the October attacks on the Arizona 911 systems, he and fellow Ben-Gurion researchers warned that DDoS attacks launched from cellphones could pose a significant threat to emergency services. During one experiment, it took fewer than 6,000 hacked phones to clog emergency services in a simulated US state, the academics wrote in a September 2016 paper. Such an attack can potentially last for days. The very nature of the 911 system makes shutting out any callers potentially dangerous, and some alternatives, like requiring a person in distress to authenticate themselves for assistance, are not viable, says Massey of DHS. “We really need to make sure that we’re not missing a critical 911 call,” he says. “So that’s a challenge for the project to make sure that we’re not misclassifying people.” Source: http://www.csmonitor.com/World/Passcode/2017/0308/How-Homeland-Security-plans-to-end-the-scourge-of-DDoS-attacks
See more here:
How Homeland Security plans to end the scourge of DDoS attacks


 The servers hosting Daphne Caruana Galizia’s personal blog have suffered a DDoS attack. A DDos (denial of service) attack occurs when many systems flood the bandwidth of a targeted system, in an attempt to make the online service unavailable. Mrs Caruana Galizia does not yet know who is behind the attack, but did say it is highly likely to be a person of Maltese nationality.. Prior to the DDoS attack on the servers, she said, a fake Gmail account was setup – similar to her personal email address. The person who created the account, then emailed two persons working for the company who handle software support for the website, and tried to acquire information required to hack the site through them. This, however, did not work and the software support personnel realised that it was not Mrs Caruana Galizia’s email address, and also the use of broken English in the email. This, she said, is what led her to believe that the person behind the attack is Maltese. The police were contacted aftewr the DDOS attack occurred later, and an investigation is ongoing. The fake Gmail address used a proxy server, and thus far no culprit has been identified, she said. She explained that aside from the crime involving the DDoS attack, impersonation is also a crime. Vanilla Communications, a server hosting company owned by David Thake, hosts Daphne Caruana Galizia’s personal blog – a service that she pays for each month, she said. In a Facebook post, Mr Thake said that the servers hosting her website suffered a DDoS attack which he called “unprecedented in scale.” Mr Thake, in his post, said the attack brought the network to its knees. Source: http://www.independent.com.mt/articles/2017-03-21/local-news/Servers-hosting-Daphne-Caruana-Galizia-s-website-suffer-unprecedented-DDOS-attack-6736171884
The servers hosting Daphne Caruana Galizia’s personal blog have suffered a DDoS attack. A DDos (denial of service) attack occurs when many systems flood the bandwidth of a targeted system, in an attempt to make the online service unavailable. Mrs Caruana Galizia does not yet know who is behind the attack, but did say it is highly likely to be a person of Maltese nationality.. Prior to the DDoS attack on the servers, she said, a fake Gmail account was setup – similar to her personal email address. The person who created the account, then emailed two persons working for the company who handle software support for the website, and tried to acquire information required to hack the site through them. This, however, did not work and the software support personnel realised that it was not Mrs Caruana Galizia’s email address, and also the use of broken English in the email. This, she said, is what led her to believe that the person behind the attack is Maltese. The police were contacted aftewr the DDOS attack occurred later, and an investigation is ongoing. The fake Gmail address used a proxy server, and thus far no culprit has been identified, she said. She explained that aside from the crime involving the DDoS attack, impersonation is also a crime. Vanilla Communications, a server hosting company owned by David Thake, hosts Daphne Caruana Galizia’s personal blog – a service that she pays for each month, she said. In a Facebook post, Mr Thake said that the servers hosting her website suffered a DDoS attack which he called “unprecedented in scale.” Mr Thake, in his post, said the attack brought the network to its knees. Source: http://www.independent.com.mt/articles/2017-03-21/local-news/Servers-hosting-Daphne-Caruana-Galizia-s-website-suffer-unprecedented-DDOS-attack-6736171884 
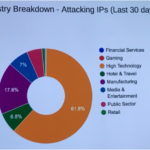 TAIPEI (Taiwan News)—Most denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks launched by hackers from Feb. 15 to March 14, 2017 in Taiwan targeted the high-tech industry, according to statistics compiled by leading global content delivery network provider Akamai Technologies. Industries in Taiwan that were most severely attacked by hackers were the high technology industry (61.8 percent), manufacturing industry (17.6 percent) and the financial services industry (7 percent), according to statistics compiled by Akamai’s intelligent platform that delivers 30 percent of the global Internet traffic. Industries in Taiwan under DDoS attacks from February 15 to March 14, 2017. (Taiwan News) The majority of the hacks were launched from IP addresses in Taiwan, followed by Alabama in the U.S., and Brazil. “It is often a misconception that most attacks are launched from abroad,” said Akamai’s Security Business Unit director Amol Mathur. “Attacks are coming both domestic and outside.” The premium CDN provider works customizes solutions for clients from different industries in Taiwan, including hospitality, banking, travel and airline services. Taiwan’s financial institutes are still recovering from a cybersecurity scare last month, in which 15 banks received threats from an anonymous hacker group to shell out 10 Bitcoins each (equivalent to US$10,466), or brace themselves for DDoS attacks that would compromise their server systems. DDoS attacks launched by hackers often compromise institute’s servers data processing capacity by delivering a sudden deluge of data that overtakes bandwidth resources, for instance if the company server bandwidth only allows 10 Gigabyte per second (Gbps) of capacity it can be paralyzed by a 100 Gbps attack. Hackers might use DDoS as a distraction to conceal other malign operations, such as stealing personal information or credential theft, added Mathur. Industries affected by hacker attacks vary monthly, depending on whether there is a major geopolitical event, said Mathur. For instance global hacker group Anonymous took down the London Stock Exchange system for two hours as part of its campaign against global central banks in June 2016. Mathur advised banks should not heed hacker demands to pay ransom. “In real life you would not pay ransom, so why would you pay hackers,” he said. The cybersecurity expert noted a rise in DDoS attacks globally during the fourth quarter of 2016, and pointed out DDoS attacks data size was increasing exponentially every quarter. Globally, attacks over 100 Gbps jumped 140 percent year-on-year during 4Q16, with the largest-size attack recorded reaching 517 Gbps, according to the Akamai “Fourth quarter 2016 State of the Internet/Security Report.” Mathur noted the cause of increased DDoS attacks was partly due to easy access for people to rent bots online, for as cheap as US$10 by going to a site and simply keying in the website address. Hackers can generate a monthly income of US$180,000 to US$200,000 from bot rentals. It remains extremely difficult for law enforcement agencies from a single country to track down hackers that spread the attacks launched by rented bots around the globe, and hide behind the protection of anonymity offered by the dark web. Additionally, the preferred Bitcoin currency used for business transactions by hackers is hard to trace to an IP address, explained Mathur. Introduction of mobile devices, mobile payment, IP surveillance cameras and emerging Internet of Things (IoT) trends introduce new cybersecurity vulnerabilities as hackers can utilize attacks through large number of connected devices. The Mirai bot for instance exposed vulnerabilities in the default user administrator name and passwords used by thousands of connected IP surveillance cameras and their DVR worldwide, said Mathur. He urged the IoT industry to form a joint standard, and for countries to start implementing regulations that set cybersecurity standards for connected devices. Hackers are also finding ways to target vulnerabilities in smartphone application programming interface (API) to obtain credentials, and data from mobile transactions. Apple Pay and some other mobile payment technologies periodically publish white papers announcing how it is securing data, but are mostly for tech savvy readers, said Mathur. One way consumers can safeguard credit card transactions is to check if the online shopping sites or App they use have The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), noted Mathur. The proprietary information security standard launched nearly a decade ago by major credit card companies Visa, MasterCard, American Express, JCB and others follows a stringent standard and heavily fines companies that do not follow its compliance. Source: http://www.taiwannews.com.tw/en/news/3117326
TAIPEI (Taiwan News)—Most denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks launched by hackers from Feb. 15 to March 14, 2017 in Taiwan targeted the high-tech industry, according to statistics compiled by leading global content delivery network provider Akamai Technologies. Industries in Taiwan that were most severely attacked by hackers were the high technology industry (61.8 percent), manufacturing industry (17.6 percent) and the financial services industry (7 percent), according to statistics compiled by Akamai’s intelligent platform that delivers 30 percent of the global Internet traffic. Industries in Taiwan under DDoS attacks from February 15 to March 14, 2017. (Taiwan News) The majority of the hacks were launched from IP addresses in Taiwan, followed by Alabama in the U.S., and Brazil. “It is often a misconception that most attacks are launched from abroad,” said Akamai’s Security Business Unit director Amol Mathur. “Attacks are coming both domestic and outside.” The premium CDN provider works customizes solutions for clients from different industries in Taiwan, including hospitality, banking, travel and airline services. Taiwan’s financial institutes are still recovering from a cybersecurity scare last month, in which 15 banks received threats from an anonymous hacker group to shell out 10 Bitcoins each (equivalent to US$10,466), or brace themselves for DDoS attacks that would compromise their server systems. DDoS attacks launched by hackers often compromise institute’s servers data processing capacity by delivering a sudden deluge of data that overtakes bandwidth resources, for instance if the company server bandwidth only allows 10 Gigabyte per second (Gbps) of capacity it can be paralyzed by a 100 Gbps attack. Hackers might use DDoS as a distraction to conceal other malign operations, such as stealing personal information or credential theft, added Mathur. Industries affected by hacker attacks vary monthly, depending on whether there is a major geopolitical event, said Mathur. For instance global hacker group Anonymous took down the London Stock Exchange system for two hours as part of its campaign against global central banks in June 2016. Mathur advised banks should not heed hacker demands to pay ransom. “In real life you would not pay ransom, so why would you pay hackers,” he said. The cybersecurity expert noted a rise in DDoS attacks globally during the fourth quarter of 2016, and pointed out DDoS attacks data size was increasing exponentially every quarter. Globally, attacks over 100 Gbps jumped 140 percent year-on-year during 4Q16, with the largest-size attack recorded reaching 517 Gbps, according to the Akamai “Fourth quarter 2016 State of the Internet/Security Report.” Mathur noted the cause of increased DDoS attacks was partly due to easy access for people to rent bots online, for as cheap as US$10 by going to a site and simply keying in the website address. Hackers can generate a monthly income of US$180,000 to US$200,000 from bot rentals. It remains extremely difficult for law enforcement agencies from a single country to track down hackers that spread the attacks launched by rented bots around the globe, and hide behind the protection of anonymity offered by the dark web. Additionally, the preferred Bitcoin currency used for business transactions by hackers is hard to trace to an IP address, explained Mathur. Introduction of mobile devices, mobile payment, IP surveillance cameras and emerging Internet of Things (IoT) trends introduce new cybersecurity vulnerabilities as hackers can utilize attacks through large number of connected devices. The Mirai bot for instance exposed vulnerabilities in the default user administrator name and passwords used by thousands of connected IP surveillance cameras and their DVR worldwide, said Mathur. He urged the IoT industry to form a joint standard, and for countries to start implementing regulations that set cybersecurity standards for connected devices. Hackers are also finding ways to target vulnerabilities in smartphone application programming interface (API) to obtain credentials, and data from mobile transactions. Apple Pay and some other mobile payment technologies periodically publish white papers announcing how it is securing data, but are mostly for tech savvy readers, said Mathur. One way consumers can safeguard credit card transactions is to check if the online shopping sites or App they use have The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), noted Mathur. The proprietary information security standard launched nearly a decade ago by major credit card companies Visa, MasterCard, American Express, JCB and others follows a stringent standard and heavily fines companies that do not follow its compliance. Source: http://www.taiwannews.com.tw/en/news/3117326