A major fork of the popular Popcorn Time project is currently being subjected to a massive DDoS attack. The whole project has been hit, from the site hosting its source through to its CDN, API and DNS servers. The team tells TorrentFreak that the attack amounts to 10Gbps across their entire network. Every year sees periods when sites in the file-sharing sector are subjected to denial of service attacks. The attackers and their motives are often unknown and eventually the assaults pass away. Early in 2014 many torrent sites were hit, pushing some offline and forcing others to invest in mitigation technology. In May a torrent related host suffered similar problems. Today it’s the turn of the main open source Popcorn Time fork to face the wrath of attackers unknown. TorrentFreak spoke with members of the project including Ops manager XeonCore who told us that the attack is massive. “We are currently mitigating a large scale DDoS attack across our entire network. We are currently rerouting all traffic via some of our high bandwidth nodes and are working on imaging and getting our remaining servers back online to help deal with the load,” the team explain. The attack is project-wide with huge amounts of traffic hitting all parts of the network, starting with the site hosting the Popcorn Time source code. Attack on the source code site – 980Mbps Also under attack is the project’s CDN and API. The graph below shows one of the project’s servers located in France. The green shows the normal traffic from the API server, the blue represents the attack. Attack on the France API server – 931Mbps Not even the project’s DNS servers have remained untouched. At one point two of three DNS servers went down, with a third straining under almost 1Gbps of traffic. To be sure, a fourth DNS server was added to assist with the load. Attack on the Dutch DNS server – peaking at 880Mbps All told the whole network is being hit with almost 10Gbps of traffic, but the team is working hard to keep things operational. “We’ve added additional capacity. Our DNS servers are currently back up and running but there is still severe congestion around Europe and America. Almost 10Gbps across the entire network. Still working on mitigating. API is still online for most users!” they conclude. Nobody has yet claimed responsibility for the attack and it’s certainly possible things will remain that way. Only time will tell when the attack will subside, but the team are determined to keep their project online in the meantime. Source: http://torrentfreak.com/popcorn-time-hit-by-massive-ddos-attack-140814/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+Torrentfreak+%28Torrentfreak%29
Read More:
Popcorn Time Hit By Massive DDoS Attack


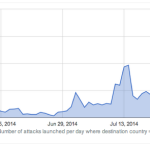 As conflict between Israel and the Palestinian militant Islamist organisation Hamas escalates, new research has revealed the impact politics has had on cyberattack trends. Tension between countries and changing political landscapes can now often be linked to cybercrime campaigns worldwide. From constant spats between the US and China to increased targeting of Syrian and Thai targets during political unrest, digital weaponry is now a key tool for groups to broadcast their own political messages, spy on governmental agencies and steal valuable data. In a new report released by Arbor Networks, anonymized traffic and DDoS attack data from over 290 ISPs that have deployed Arbor’s Peakflow SP product — collated and analyzed as part of Arbor’s ATLAS initiative — it appears that DDoS attacks are rising in number and volume as a result of the Israel-Hamas conflict. The graph below depicts the number of reported DDoS attacks initiated against Israel daily over the 1 June to 3 August period this year: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are used to flood a website or service with traffic to the point systems cannot cope, denying other users access to the website. Arbor detected a rise in the number of DDoS attacks targeting Israel in the first week of July, going from an average of 30 attacks per day to an average of 150 attacks initiated per day in July — peaking at 429 attacks on July 21st. Linking these cyberattacks to political situations, 30 June is when Israel publicly attributed the deaths of three kidnapped Israeli teenagers to Hamas, and on 7 July, “Operation Protective Edge” was launched by the country. As the political conflict raged on, so did the frequency of DDoS attacks until a drop occurred on 28 July lasting through 2 August. Arbor says the drop in attacks roughly correlates with cease fire talks which began 27 July. From 28 July through 2 August, there were 192 attacks recorded in total. On 3 August, the number of DDoS attacks rose sharply, with 268 attacks in total. In addition to the number of DDoS attacks over these time periods, the security researchers also noticed an increase in the peak size of these attacks. In the graph below, we can see that in June, no attacks exceeded 12Gbps. In July, seven DDoS attacks exceeded this size, with the largest peaking at 22.56Gbps on 12 July. When cease-fire talks fell apart on 3 August, the largest DDoS attack was recorded at a size of 29Gbps. The duration of DDoS attacks has also increased. In June, the average duration was 20 minutes — with a peak duration of 24 hours — and in July, the average duration was 1 hour 39 minutes. “As the intensity of the Israeli-Hamas conflict has increased, so has the number, size and duration of the DDoS attacks targeting Israel,” the researchers say. “Additionally, it even appears as if the attackers have made an effort to adhere to the “real world” calls for a cease-fire, resuming their attacks when the cease fire fell through.” Source: http://www.zdnet.com/israel-hamas-conflict-sparks-surge-in-ddos-attacks-7000032375/#ftag=RSS14dc6a9
As conflict between Israel and the Palestinian militant Islamist organisation Hamas escalates, new research has revealed the impact politics has had on cyberattack trends. Tension between countries and changing political landscapes can now often be linked to cybercrime campaigns worldwide. From constant spats between the US and China to increased targeting of Syrian and Thai targets during political unrest, digital weaponry is now a key tool for groups to broadcast their own political messages, spy on governmental agencies and steal valuable data. In a new report released by Arbor Networks, anonymized traffic and DDoS attack data from over 290 ISPs that have deployed Arbor’s Peakflow SP product — collated and analyzed as part of Arbor’s ATLAS initiative — it appears that DDoS attacks are rising in number and volume as a result of the Israel-Hamas conflict. The graph below depicts the number of reported DDoS attacks initiated against Israel daily over the 1 June to 3 August period this year: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are used to flood a website or service with traffic to the point systems cannot cope, denying other users access to the website. Arbor detected a rise in the number of DDoS attacks targeting Israel in the first week of July, going from an average of 30 attacks per day to an average of 150 attacks initiated per day in July — peaking at 429 attacks on July 21st. Linking these cyberattacks to political situations, 30 June is when Israel publicly attributed the deaths of three kidnapped Israeli teenagers to Hamas, and on 7 July, “Operation Protective Edge” was launched by the country. As the political conflict raged on, so did the frequency of DDoS attacks until a drop occurred on 28 July lasting through 2 August. Arbor says the drop in attacks roughly correlates with cease fire talks which began 27 July. From 28 July through 2 August, there were 192 attacks recorded in total. On 3 August, the number of DDoS attacks rose sharply, with 268 attacks in total. In addition to the number of DDoS attacks over these time periods, the security researchers also noticed an increase in the peak size of these attacks. In the graph below, we can see that in June, no attacks exceeded 12Gbps. In July, seven DDoS attacks exceeded this size, with the largest peaking at 22.56Gbps on 12 July. When cease-fire talks fell apart on 3 August, the largest DDoS attack was recorded at a size of 29Gbps. The duration of DDoS attacks has also increased. In June, the average duration was 20 minutes — with a peak duration of 24 hours — and in July, the average duration was 1 hour 39 minutes. “As the intensity of the Israeli-Hamas conflict has increased, so has the number, size and duration of the DDoS attacks targeting Israel,” the researchers say. “Additionally, it even appears as if the attackers have made an effort to adhere to the “real world” calls for a cease-fire, resuming their attacks when the cease fire fell through.” Source: http://www.zdnet.com/israel-hamas-conflict-sparks-surge-in-ddos-attacks-7000032375/#ftag=RSS14dc6a9