Hacktivist group Anonymous has continued to add to its list of targets, with controversial US presidential candidate Donald Trump the latest in the crosshairs. Following Trump’s radical speech stating he wanted to ban Muslims from entering the US, Twitter accounts linked to the group declared war. The OpTrump campaign launched last night (9 December) with the first piece of business taking down Trump’s website www.trumptowerny.com for several hours by hitting it with a DDOS (distributed-denial-of-service) attack, which crashed the site. One Twitter user posted a picture of the hack, claiming the site was “almost down”. Anonymous posted a video online in response to Trump’s comments and warned of the repercussions of his words. “Donald Trump, it has come to our attention that you want to ban all Muslims from entering the United States. This policy is going to have a huge impact. This is what Isis wants. The more Muslims feel sad the more Isis feels they can recruit them. The more the United States appears to be targeting Muslims, not just radical Muslims you can be sure Isis will be putting that on their social media campaign,” said a masked member of the hacktivist group. While Anonymous has yet to officially claim responsibility for the DDOS attack, Twitter users showed full support of the group and its campaign. In the grand scheme of things this was a fairly tame attack, as the website is still running as normal at the time of writing, but it did serve as a digital slap to show this could be the first of many targeted operations against Trump. Anonymous is also busy taking on Islamic State by organising an official Isis Trolling Day called “Day of Rage” on 11 December, where it is encouraging an uprising of social media users to post content mocking the terror group. They issued a list of actions in a statement that includes reporting accounts of Isis sympathisers, posting mocking photos and use mocking hashtags. There will also be organised demonstrations held around the world. Source: http://www.ibtimes.co.uk/optrump-anonymous-declares-war-donald-trump-ddos-attack-following-muslim-ban-speech-1532739
Read more here:
OpTrump: Anonymous declares war on Donald Trump with DDOS attack following Muslim ban speech


 Cyber-crime syndicates are moving in, pushing script kiddies out of the picture, expect more large-scale attacks After the success of DDoSing outfits like DD4BC and Armada Collective, an unknown copycat that’s using the Armada Collective name but asking for astronomical payments has appeared. A report from Recorded Future, a real-time threat intelligence protection company, shows that DDoS-for-Bitcoin extortion schemes are here to stay, with more and more attacks being launched solely for this reason. DD4BC have launched a new type of extortion scheme This trend can be tracked down to an Akamai report released over the summer that documented the actions of a hacking group known as DD4BC (DDoS 4 Bitcoin). This group launched DDoS attacks on companies around the world, requesting small payments in Bitcoin for each target. The group’s scheme was a simple one. They would send threatening emails to business owners, saying they would launch powerful DDoS attacks if a ransom was not paid in due time to a specific Bitcoin wallet. To prove their point, a small 15-minute DDoS was launched to showcase their capabilities. DD4BC’s scheme proved to be extremely lucrative and allowed them to rack up Bitcoin over the past year in over 140 DDoS attacks. The group was active since late 2014 and suddenly stopped its activity after the Akamai report was released, probably to avoid getting caught by law enforcement authorities alerted to their scheme. Enter Armada Collective Soon after, the first DD4BC copycat arose, in the form of the Armada Collective hackers, carrying out DDoS attacks on small businesses in Switzerland. They then expanded to email providers, and their name became known around the world in the famous ProtonMail incident. The incident is very well documented in one of our previous stories , but we’ll give you a small summary. Basically, Armada Collective followed the DD4BC regular tactics, sending an email and launching a small 10-15 Gbps DDoS attack on ProtonMail. Armada Collective returning ransom to ProtonMail As soon as the attack ended, ProtonMail revealed what happened, and more serious attacks took place, with ProtonMail paying the ransom in the end. Armada Collective denied any involvement and even went as far as to return the ProtonMail ransom, putting the blame on a state-sponsored actor with capabilities that far exceeded its own. Enter the unknown copycat But something else happened recently that made the Recorded Future team stop and ponder about the bigger picture, and that’s the DDoS-for-Bitcoin attacks on three major Greek banks . With DD4BC and Armada Collective always launching small-scale attacks and requesting modest ransoms (the equivalent of a few thousand dollars), this new group attacking Greek banks does not fit the bill. While the attacks of DD4BC and Armada Collective seem to be the work of script kiddies, the ones that brought down ProtonMail and the three major Greek banks were massive in scale. Coupled with the fact that this new group also requests ransoms in the order of millions of dollars, there are clear signs that they are a copycat that’s trying to remain hidden by passing as Armada Collective (as stated in the email sent to the Greek banks). With the number of DDoS-for-Bitcoin attacks on the rise, this type of cyber-threat is about to evolve from the work of script kiddies to the normal MO of larger cyber-criminal syndicates.
Cyber-crime syndicates are moving in, pushing script kiddies out of the picture, expect more large-scale attacks After the success of DDoSing outfits like DD4BC and Armada Collective, an unknown copycat that’s using the Armada Collective name but asking for astronomical payments has appeared. A report from Recorded Future, a real-time threat intelligence protection company, shows that DDoS-for-Bitcoin extortion schemes are here to stay, with more and more attacks being launched solely for this reason. DD4BC have launched a new type of extortion scheme This trend can be tracked down to an Akamai report released over the summer that documented the actions of a hacking group known as DD4BC (DDoS 4 Bitcoin). This group launched DDoS attacks on companies around the world, requesting small payments in Bitcoin for each target. The group’s scheme was a simple one. They would send threatening emails to business owners, saying they would launch powerful DDoS attacks if a ransom was not paid in due time to a specific Bitcoin wallet. To prove their point, a small 15-minute DDoS was launched to showcase their capabilities. DD4BC’s scheme proved to be extremely lucrative and allowed them to rack up Bitcoin over the past year in over 140 DDoS attacks. The group was active since late 2014 and suddenly stopped its activity after the Akamai report was released, probably to avoid getting caught by law enforcement authorities alerted to their scheme. Enter Armada Collective Soon after, the first DD4BC copycat arose, in the form of the Armada Collective hackers, carrying out DDoS attacks on small businesses in Switzerland. They then expanded to email providers, and their name became known around the world in the famous ProtonMail incident. The incident is very well documented in one of our previous stories , but we’ll give you a small summary. Basically, Armada Collective followed the DD4BC regular tactics, sending an email and launching a small 10-15 Gbps DDoS attack on ProtonMail. Armada Collective returning ransom to ProtonMail As soon as the attack ended, ProtonMail revealed what happened, and more serious attacks took place, with ProtonMail paying the ransom in the end. Armada Collective denied any involvement and even went as far as to return the ProtonMail ransom, putting the blame on a state-sponsored actor with capabilities that far exceeded its own. Enter the unknown copycat But something else happened recently that made the Recorded Future team stop and ponder about the bigger picture, and that’s the DDoS-for-Bitcoin attacks on three major Greek banks . With DD4BC and Armada Collective always launching small-scale attacks and requesting modest ransoms (the equivalent of a few thousand dollars), this new group attacking Greek banks does not fit the bill. While the attacks of DD4BC and Armada Collective seem to be the work of script kiddies, the ones that brought down ProtonMail and the three major Greek banks were massive in scale. Coupled with the fact that this new group also requests ransoms in the order of millions of dollars, there are clear signs that they are a copycat that’s trying to remain hidden by passing as Armada Collective (as stated in the email sent to the Greek banks). With the number of DDoS-for-Bitcoin attacks on the rise, this type of cyber-threat is about to evolve from the work of script kiddies to the normal MO of larger cyber-criminal syndicates. 
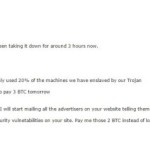 Two sister blogs, Hacked (Security & Tech) and CryptoCoinsNews, have decided to go the Mel Gibson route (“Ransom” movie reference for the uncool kids) and put out a bounty on DDoS attackers instead of paying the money they were asking for. It all started earlier this morning, when both sites saw a serious DDoS attack being carried out against their server infrastructure. Three hours after the attack began, the two received emails from a man named Jon. The attacker claimed to own a botnet that he intended to use for DDoS attacks. He said that currently he was using only 20% of the botnet’s capabilities against the two sites. Jon was asking for a 2 Bitcoin ransom, which would become 3 Bitcoin by tomorrow if unpaid. Instead of giving in and being intimidated by the attacker, the two sites ramped up their DDoS mitigation and decided to put out a 5 Bitcoin ransom on the attacker, which is about $1,600 or €1,500 in today’s exchange rate. Turning the table on DDoS extortionists “If you can help us identify the extortionists in a way that leads to a successful police report, you will receive five bitcoins, with gratitude,” says Samburaj Das of CCN and Hacked. The bloggers are looking for data like real names, addresses, and attacks carried out on other sites that would allow investigators to track their DDoS campaign. Details should be sent to crypto@cryptocoinsnews.com. Only last month something similar happened to ProtonMail, a crypto email service. The site was under a massive DDoS attack, which also expanded to its ISP. Due to peer pressure from other affected services, ProtonMail paid the ransom , but the attacks never stopped, with other groups also taking aim at their infrastructure. Many people skewered ProtonMail’s owners for paying the attackers, saying it was a bad idea and did nothing but encourage such types of groups to carry on with their DDoS-for-Bitcoin extortion campaigns . We’ll just have to wait and see how Hacked/CCN’s countermove goes through. Source: http://news.softpedia.com/news/bloggers-put-bounty-on-ddos-extortionists-496586.shtml
Two sister blogs, Hacked (Security & Tech) and CryptoCoinsNews, have decided to go the Mel Gibson route (“Ransom” movie reference for the uncool kids) and put out a bounty on DDoS attackers instead of paying the money they were asking for. It all started earlier this morning, when both sites saw a serious DDoS attack being carried out against their server infrastructure. Three hours after the attack began, the two received emails from a man named Jon. The attacker claimed to own a botnet that he intended to use for DDoS attacks. He said that currently he was using only 20% of the botnet’s capabilities against the two sites. Jon was asking for a 2 Bitcoin ransom, which would become 3 Bitcoin by tomorrow if unpaid. Instead of giving in and being intimidated by the attacker, the two sites ramped up their DDoS mitigation and decided to put out a 5 Bitcoin ransom on the attacker, which is about $1,600 or €1,500 in today’s exchange rate. Turning the table on DDoS extortionists “If you can help us identify the extortionists in a way that leads to a successful police report, you will receive five bitcoins, with gratitude,” says Samburaj Das of CCN and Hacked. The bloggers are looking for data like real names, addresses, and attacks carried out on other sites that would allow investigators to track their DDoS campaign. Details should be sent to crypto@cryptocoinsnews.com. Only last month something similar happened to ProtonMail, a crypto email service. The site was under a massive DDoS attack, which also expanded to its ISP. Due to peer pressure from other affected services, ProtonMail paid the ransom , but the attacks never stopped, with other groups also taking aim at their infrastructure. Many people skewered ProtonMail’s owners for paying the attackers, saying it was a bad idea and did nothing but encourage such types of groups to carry on with their DDoS-for-Bitcoin extortion campaigns . We’ll just have to wait and see how Hacked/CCN’s countermove goes through. Source: http://news.softpedia.com/news/bloggers-put-bounty-on-ddos-extortionists-496586.shtml