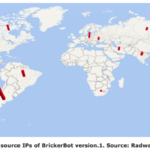
 Canada is among the countries that have been stung by a mysterious botnet infecting Internet-connected devices using the Linux and BusyBox operating systems that essentially trashes the hardware, according to a security vendor. Called a Permanent Denial of Service attack (PDoS) – also called “plashing” by some – the attack exploits security flaws or misconfiguration and goes on to destroy device firmware and/or basic functions of a system, Radware said in a blog released last week. The first of two versions has rendered IoT devices affected into bricks, which presumably is why the attack has been dubbed the BrickerBot. A second version goes after IoT devices and Linux servers. “Over a four-day period, Radware’s honeypot recorded 1,895 PDoS attempts performed from several locations around the world,” the company said in the blog. “Its sole purpose was to compromise IoT devices and corrupt their storage.” After accessing a device by brute force attacks on the Telnet login, the malware issues a series of Linux commands that will lead to corrupted storage, followed by commands to disrupt Internet connectivity, device performance, and the wiping of all files on the device. Vulnerable devices have their Telnet port open. Devices tricked into spreading the attack — mainly equipment from Ubiquiti Networks Inc. including wireless access points and bridges with beam directivity — ran an older version of the Dropbear secure shell (SSH) server. Radware estimates there are over 20 million devices with Dropbear connected to the Internet now which could be leveraged for attacks. Targets include digital video cameras and recorders, which have also been victimized by the Mirai or similar IoT botnets. According to Radware, the PDoS attempts it detected came from a limited number of IP addresses in Argentina, the U.S., Canada, Russia, Iran, India, South Africa and other countries. Two versions of the bot were found starting March 20: Version one, which was short-lived and aimed at BusyBox devices, and version two, which continues and has a wider number of targets. While the IP addresses of servers used to launch the first attack can be mapped, the more random addresses of servers used in the second attack have been obscured by Tor egress nodes. The second version is not only going after IoT devices but also Unix and Linux servers by adding new commands. What makes this botnet mysterious is that it wipes out devices, rather than try to assemble them into a large dagger that can knock out web sites – like Mirai. “BrickerBot 2 is still ongoing,” Pascal Geenens, a Radware security evangelist based in Belgium, said in a phone interview this morning. “We still don’t have an idea who it is because it’s still hiding behind the Tor network.” “We still have a lot of questions like where was it originating from, what is the motivation? One of them could be someone who’s angry at IoT manufacturers for not solving that [security] problem, maybe somebody who suffered a DDoS attack and wants to get back at manufacturers by bricking the devices. That way it solves the IoT problem and gets back at manufacturers. “Another idea that I have is maybe its a hacker that is running Windows-based botnets, which are more costly to maintain.” It’s easy to inspect and compromise an IoT device through a Telnet command, he explained, so IoT botnet are easy to assemble. That lowers the cost for a botnet-for-hire. By comparison Windows devices have to be compromised through phishing campaigns that trick end users into downloading binaries that evade anti-virus software. It’s complex. So Geenens wonders if a hacker’s goal here is to get into IoT botnets and destroy the devices, which then raises the value of his Windows botnet. Another theory is the attacker is searching for Linux-based honeypots — traps set by infosec pros — with default passwords. He also pointed out Unix or Linux-based servers with default credentials are vulnerable to the BrickerBot 2 attack. However, he added, there wouldn’t be many of those because during installation process Linux ask for creation of a root password, so there isn’t a default credential. The exception, he added, is a pre-installed image downloaded from the Internet. Administrators who have these devices on their networks are urged to change factory default credentials and disable Telnet access. Network and user behavior analysis can detect anomalies in traffic, says Radware. Source: http://www.itworldcanada.com/article/canada-one-of-sources-for-destructive-iot-botnet/392242
Canada is among the countries that have been stung by a mysterious botnet infecting Internet-connected devices using the Linux and BusyBox operating systems that essentially trashes the hardware, according to a security vendor. Called a Permanent Denial of Service attack (PDoS) – also called “plashing” by some – the attack exploits security flaws or misconfiguration and goes on to destroy device firmware and/or basic functions of a system, Radware said in a blog released last week. The first of two versions has rendered IoT devices affected into bricks, which presumably is why the attack has been dubbed the BrickerBot. A second version goes after IoT devices and Linux servers. “Over a four-day period, Radware’s honeypot recorded 1,895 PDoS attempts performed from several locations around the world,” the company said in the blog. “Its sole purpose was to compromise IoT devices and corrupt their storage.” After accessing a device by brute force attacks on the Telnet login, the malware issues a series of Linux commands that will lead to corrupted storage, followed by commands to disrupt Internet connectivity, device performance, and the wiping of all files on the device. Vulnerable devices have their Telnet port open. Devices tricked into spreading the attack — mainly equipment from Ubiquiti Networks Inc. including wireless access points and bridges with beam directivity — ran an older version of the Dropbear secure shell (SSH) server. Radware estimates there are over 20 million devices with Dropbear connected to the Internet now which could be leveraged for attacks. Targets include digital video cameras and recorders, which have also been victimized by the Mirai or similar IoT botnets. According to Radware, the PDoS attempts it detected came from a limited number of IP addresses in Argentina, the U.S., Canada, Russia, Iran, India, South Africa and other countries. Two versions of the bot were found starting March 20: Version one, which was short-lived and aimed at BusyBox devices, and version two, which continues and has a wider number of targets. While the IP addresses of servers used to launch the first attack can be mapped, the more random addresses of servers used in the second attack have been obscured by Tor egress nodes. The second version is not only going after IoT devices but also Unix and Linux servers by adding new commands. What makes this botnet mysterious is that it wipes out devices, rather than try to assemble them into a large dagger that can knock out web sites – like Mirai. “BrickerBot 2 is still ongoing,” Pascal Geenens, a Radware security evangelist based in Belgium, said in a phone interview this morning. “We still don’t have an idea who it is because it’s still hiding behind the Tor network.” “We still have a lot of questions like where was it originating from, what is the motivation? One of them could be someone who’s angry at IoT manufacturers for not solving that [security] problem, maybe somebody who suffered a DDoS attack and wants to get back at manufacturers by bricking the devices. That way it solves the IoT problem and gets back at manufacturers. “Another idea that I have is maybe its a hacker that is running Windows-based botnets, which are more costly to maintain.” It’s easy to inspect and compromise an IoT device through a Telnet command, he explained, so IoT botnet are easy to assemble. That lowers the cost for a botnet-for-hire. By comparison Windows devices have to be compromised through phishing campaigns that trick end users into downloading binaries that evade anti-virus software. It’s complex. So Geenens wonders if a hacker’s goal here is to get into IoT botnets and destroy the devices, which then raises the value of his Windows botnet. Another theory is the attacker is searching for Linux-based honeypots — traps set by infosec pros — with default passwords. He also pointed out Unix or Linux-based servers with default credentials are vulnerable to the BrickerBot 2 attack. However, he added, there wouldn’t be many of those because during installation process Linux ask for creation of a root password, so there isn’t a default credential. The exception, he added, is a pre-installed image downloaded from the Internet. Administrators who have these devices on their networks are urged to change factory default credentials and disable Telnet access. Network and user behavior analysis can detect anomalies in traffic, says Radware. Source: http://www.itworldcanada.com/article/canada-one-of-sources-for-destructive-iot-botnet/392242
Read the original:
Canada one of sources for destructive IoT botnet

