Cybersecurity has become a significant issue as attacks are increasing. In the new payments ecosystem, where third-party developers can directly interact with banks’ customers, data privacy and security become paramount, according to the World Payments Report 2017 by Capgemini and BNP Paribas . A significant issue to address as the new payments ecosystem evolves is that of cybersecurity. During the past few years, cyberattacks and crimes have increased across the globe, with corporate and financial institution entities, large and small, targeted. The price of increasing collaboration among industry stakeholders in the new payments ecosystem could be an increase in cyber security vulnerabilities. To alleviate this risk, corporates are increasingly turning to their banks for advice on how to strengthen their infrastructures against cyber attacks. To ensure the highest levels of cybersecurity and the security of infrastructures in the new payments ecosystem, each stakeholder must assess security across all the data sources and points of collaboration. The need for robust cyber security solutions to cater to all forms of cyberthreats has never been greater for corporate treasurers as new technologies proliferate and collaboration increases. Of prime importance for corporates in developing defence mechanisms is awareness of potential cyber security risks, regular updating of security profiles and continuous training of employees. This is because attacks perpetrated by cybercriminals are unpredictable in both timing and nature. The vulnerabilities stakeholders face include cyber security, data privacy, data breaches, and payments fraud. The utmost vigilance is required to protect organisations against cyber attacks and all stakeholders, including regulators, must be more proactive regarding cybersecurity, with ownership of the issue taken to prevent attacks. In the new payments ecosystem, third-party developers can directly interact with a partner banks’ customers, raising questions about data privacy and security. In an increasingly networked ecosystem, identifying the source of attack will be a challenge. Verizon’s 2017 Data Breach Investigations Report found that security incidents and data breaches affect both large and small financial organisations almost equally. However, the security of larger banks is difficult to compromise as they invest more in cyber security solutions. Smaller banks, which do not have the same access to resources, are more prone to cyberattacks. A fraud survey by the Association for Financial Professionals and JP Morgan found that the highest levels of fraud in 2016 were perpetrated via cheques. However, there was a surge in wire transfer fraud, from 27 per cent in 2014 to 46 per cent in 2016. An increasing number of cyber security breaches are causing significant losses for banks and corporates across the world. Among recent incidents, in February 2016, a cyberheist at Bangladesh Central Bank resulted in a loss of $81 million and prevented another $850 million worth of transactions from being processed on the Swift network. Similarly, in May 2016 cybercriminals hacked the Swift system and stole $9 million from Ecuadorian bank Banco del Austro. In May 2017, the WannaCry ransomware attack affected more than 150 countries and 200,000 computers, as attackers demanded each of those affected to pay up to $300 worth of bitcoins to unlock their systems. In a survey for World Payments Report , bank executives ranked distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks and customer payments fraud as the main security challenges they face. Also of concern were the high levels of card fraud, which place a significant cost burden on banks. The increasing adoption of digital offerings in transaction banking is also giving rise to higher levels of payments fraud, making cyber security a top priority for banks and corporates. Customer payments fraud is the top ranked concern for financial technology companies and other survey respondents. This group is much less likely to view DDoS attacks as a threat; data breaches due to hacking attacks was of more concern, as was internal fraud. While banks are investing significantly in cybersecurity solutions, there are still many risks at the corporate level that they cannot manage. Corporates must, therefore, step up their own efforts to manage cybersecurity risk and not leave it all to the banks. They should upgrade their internal systems, train their staff, and review their partners’ systems. The idea of a cyberattacker as a lone figure hacking into systems is now obsolete. Cyberattacks are perpetrated by entities that are set up like companies, with project managers, key performance indicators and operations. Attacks to compromise corporates and banks are designed to be multi-staged, with two main objectives: commercial gain and industry espionage. In general, the funds received via attacks go into the coffers of the organisation, while the intelligence gained during an attack will be used by perpetrators to gain a business advantage. Attacks can happen at any time, and over time, therefore all corporates should be vigilant and on constant guard against attacks. So serious are the growing cyberattack and data breach problems that regulators across the globe should move from their present reactive approach to a more proactive one. Stringent regulations and fines to strengthen cybersecurity laws are required from regulators. Many regulations related to this are, however, still in the inception stage. Europe has relatively the most mature cybersecurity and data privacy laws, with recent initiatives including the Electronic Identification and Trusted Service which was launched in 2016. Effective cybersecurity requires organisations to efficiently and quickly identify, mitigate and manage cyber risks and incidents. All stakeholders are taking measures to strengthen the security of transactions against potential cyber threats. Banks and other stakeholders have three options available to them: collaborating with financial technology companies, making investments in advanced technologies and monitoring tools, and strengthening internal governance to ensure seamless compliance. Collaboration with fintechs This is occurring in several areas including secure authentication and authorisation, account onboarding, identity verification and anti-money laundering. Examples include India’s Yes Bank and FortyTwoLabs’ development of multi-factor authentication tool PI-Control, which enables users to apply for internet banking access, pay bills, transfer funds, seek loans, make remittances and undertake other card transactions. Rabobank in the Netherlands is working with Signicat to provide digital identity solutions that can be easily integrated using API technology. As banks increasingly collaborate with fintechs and regtechs, due diligence, adherence to industry standards and participating in the development of new industry standards has become critical. Investment in advanced technologies and monitoring tools Blockchain technology is still in a nascent stage, with its potential as an enabler of digital identity and payment transaction security still being tested. Banks can leverage the technology to differentiate themselves in the provision of digital identity, authentication and know your customer services. Banks are investing in projects that combine advanced cryptography that supports private or permitted use of blockchain technology with transaction security elements that provider greater transaction visibility. To ensure the highest levels of cybersecurity and transaction security, all the ecosystem participants must assess security from multiple sources in the network. Common security standards and protocols when developing and investing in new technologies and monitoring tools will be increasingly important as collaboration increases. With a common network governing the interfaces between banks and third-party providers, various groups are developing network-based security standards to ensure a secure environment is built around the dynamic payments ecosystem. The ability to respond to cyber threats or attacks in real-time is hampered by legacy security systems. Traditional security monitoring typically identified and reacted to cyber threats in isolation. A modern approach identifies specific unusual patterns or behaviour and alerts operational teams to anomalous activity. Advanced machine learning algorithms are the logical next step as response mechanisms in the event of a threat. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems are being piloted globally, yet legal issues regarding accountability for the actions of such systems persist. Contextualisation of threats (linking the threat to the business and not just to technology) is needed to identify the source and understand the objective behind any attack. Another useful approach is risk-based authentication (RBA) to detect the risk profile of transaction banks and retailers. Using RBA and analytics processes, banks can create a threat matrix of fraud profiles to triangulate the threat instances to their origin and be able to proactively block fraudulent traffic. Behavioural analytics, AI, machine learning and threat matrix can help to continuously monitor the ecosystem network and provide threat intelligence. Banks can undertake various activities such as continuously checking all systems for possible threats, observing markets, scenario simulation, examination of previous attacks, monitoring activities and applications, and establishing a payments control centre to permanently monitor payments and identify exceptional situations. Robust internal governance A robust governance model and standards are imperative for seamless functioning of the new payments ecosystem. Banks and treasurers need to interact with central authorities and regulators to share feedback, which in turn will help to improve compliance. Banks and treasurers are increasingly collaborating with regtechs to ensure compliance. Industry stakeholders must establish common data, technical, legal, functional, and security standards for robust governance. Firms will be well served if they can ensure that security systems have multiple layers to withstand ‘flood’ attacks. To ensure a foolproof system, firms should identify the data needs of all stakeholders before finalising the controls to put in place. With the onset of General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) in the EU, the focus on compliance with data privacy and security has increased. Firms must install a dedicated team to continuously review and update security policies. Additionally, stakeholders should work with the local regulatory authorities to understand the complexity of different regional legal requirements and expectations for each country. Firms must ensure mandatory data privacy and security training is conducted at regular intervals. Educating employees on potential threats and ensuring they keep their systems updated would have prevented, or greatly reduced the impact of, events such as the WannaCry ransomware attack. Source: http://www.bankingtech.com/1019032/cybersecurity-into-the-data-breach/
View article:
Cybersecurity: into the data breach


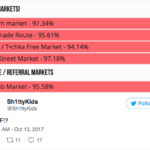 There seems to be some turbulence going on in the murky world of the dark web, with four of its major drug marketplaces unexpectedly going offline, reports said. The dark web is a section of the internet where people contact each other anonymously without the fear of being monitored. It is usually used by criminals to sell drugs, chemicals, weapons, child abuse images and even offer assassination services. Websites The Trade Route, Tochka, Wall Street Market and Dream Market, were down without any notification or clarification from the sites’ administrators. According to some users of such markets, this might either be a DDoS attack by a hacker or a large scale action by law enforcement authorities. However, there are more chances of the former happening than the latter. Some dark web users have also started complaining of botnet attacks. Another farfetched theory is that this is scam by a bunch of drug dealers — taking off with the money of their clients while not providing them with the required merchandize. With no notification or clarification from the sites’ administrators, the exact reason for the sudden disappearance of such marketplaces remains unclear. However, a user going by the name Automoderator commented on a the subreddit /r/DarkNetMarketNoobs that the WallStreetMarket is not listed currently, as it is facing “very serious issues” and warned others to avoid it all costs. Some other users on the subreddit say that the Dream Market has been working fine on all its mirrors, but, however its main site is down. At the time of writing, the marketplaces were still down, according to dark web marketplace tracker deepdotweb. Many sites on the dark web are also run by law enforcement — the Australian Police ran one of the world’s biggest child porn sites on the dark web between October 2016 and September 2017, called Child’s Play, in an effort to nab pedophiles. The police grabbed the administrator access from two cyber criminals — Benjamin Faulkner and Patrick Falte and started administering the sites. Police even posted more child porn on the site in an effort to convince the viewers that the site had not been taken over by the authorities. By the time they shut down the site, police were able to nab more than 90 pedophiles in Australia and 900 across the world. In case, the marketplaces were being taken over by law enforcement to nab drug traffickers and child porn purveyors, it might be a different case. However the development has many dark web users in a state of paranoia and many users have posted on Reddit reminding other users of such busts. Such attacks on dark web markets in the past have usually begun with large-scale DDoS attacks. In July, a massive trans-continental sting saw two of the dark web’s biggest sites at the time, AlphaBay and Hansa, being taken down. Law enforcement agencies claimed they were able to collect incriminating information on hundreds of buyers and vendors, going as far as threatening to prosecute them. Source: http://www.ibtimes.com/dark-web-marketplaces-go-down-reported-mass-ddos-attack-2601105
There seems to be some turbulence going on in the murky world of the dark web, with four of its major drug marketplaces unexpectedly going offline, reports said. The dark web is a section of the internet where people contact each other anonymously without the fear of being monitored. It is usually used by criminals to sell drugs, chemicals, weapons, child abuse images and even offer assassination services. Websites The Trade Route, Tochka, Wall Street Market and Dream Market, were down without any notification or clarification from the sites’ administrators. According to some users of such markets, this might either be a DDoS attack by a hacker or a large scale action by law enforcement authorities. However, there are more chances of the former happening than the latter. Some dark web users have also started complaining of botnet attacks. Another farfetched theory is that this is scam by a bunch of drug dealers — taking off with the money of their clients while not providing them with the required merchandize. With no notification or clarification from the sites’ administrators, the exact reason for the sudden disappearance of such marketplaces remains unclear. However, a user going by the name Automoderator commented on a the subreddit /r/DarkNetMarketNoobs that the WallStreetMarket is not listed currently, as it is facing “very serious issues” and warned others to avoid it all costs. Some other users on the subreddit say that the Dream Market has been working fine on all its mirrors, but, however its main site is down. At the time of writing, the marketplaces were still down, according to dark web marketplace tracker deepdotweb. Many sites on the dark web are also run by law enforcement — the Australian Police ran one of the world’s biggest child porn sites on the dark web between October 2016 and September 2017, called Child’s Play, in an effort to nab pedophiles. The police grabbed the administrator access from two cyber criminals — Benjamin Faulkner and Patrick Falte and started administering the sites. Police even posted more child porn on the site in an effort to convince the viewers that the site had not been taken over by the authorities. By the time they shut down the site, police were able to nab more than 90 pedophiles in Australia and 900 across the world. In case, the marketplaces were being taken over by law enforcement to nab drug traffickers and child porn purveyors, it might be a different case. However the development has many dark web users in a state of paranoia and many users have posted on Reddit reminding other users of such busts. Such attacks on dark web markets in the past have usually begun with large-scale DDoS attacks. In July, a massive trans-continental sting saw two of the dark web’s biggest sites at the time, AlphaBay and Hansa, being taken down. Law enforcement agencies claimed they were able to collect incriminating information on hundreds of buyers and vendors, going as far as threatening to prosecute them. Source: http://www.ibtimes.com/dark-web-marketplaces-go-down-reported-mass-ddos-attack-2601105