Attacks came from either an unusual type of DDoS or poorly written spam bots. On May 8, when the Federal Communications Commission website failed and many people were prevented from submitting comments about net neutrality, the cause seemed obvious. Comedian John Oliver had just aired a segment blasting FCC Chairman Ajit Pai’s plan to gut net neutrality rules, and it appeared that the site just couldn’t handle the sudden influx of comments. But when the FCC released a statement explaining the website’s downtime, the commission didn’t mention the Oliver show or people submitting comments opposing Pai’s plan. Instead, the FCC attributed the downtime solely to “multiple distributed denial-of-service attacks (DDoS).” These were “deliberate attempts by external actors to bombard the FCC’s comment system with a high amount of traffic to our commercial cloud host,” performed by “actors” who “were not attempting to file comments themselves; rather, they made it difficult for legitimate commenters to access and file with the FCC.” The FCC has faced skepticism from net neutrality activists who doubt the website was hit with multiple DDoS attacks at the same time that many new commenters were trying to protest the plan to eliminate the current net neutrality rules. Besides the large influx of legitimate comments, what appeared to be spam bots flooded the FCC with identical comments attributed to people whose names were drawn from data breaches, which is another possible cause of downtime. There are now more than 2.5 million comments on Pai’s plan. The FCC is taking comments until August 16 and will make a final decision some time after that. The FCC initially declined to provide more detail on the DDoS attacks to Ars and other news organizations, but it is finally offering some more information. A spokesperson from the commission’s public relations department told Ars that the FCC stands by its earlier statement that there were multiple DDoS attacks. An FCC official who is familiar with the attacks suggested they might have come either from a DDoS or spam bots but has reason to doubt that they were just spam bots. In either case, the FCC says the attacks worked differently from traditional DDoSes launched from armies of infected computers. A petition by activist group Fight for the Future suggests that the FCC “invent[ed] a fake DDoS attack to cover up the fact that they lost comments from net neutrality supporters.” But while FCC commissioners are partisan creatures who are appointed and confirmed by politicians, the commission’s IT team is nonpartisan, with leadership that has served under both Presidents Obama and Trump. There’s no consensus among security experts on whether May 8 was or wasn’t the result of a DDoS attack against the FCC comments site. One security expert we spoke to said it sounds like the FCC was hit by an unusual type of DDoS attack, while another expert suggested that it might have been something that looked like a DDoS attack but actually wasn’t. Breaking the silence FCC CIO David Bray offered more details on how the attack worked in an interview with ZDNet published Friday. Here’s what the article said: According to Bray, FCC staff noticed high comment volumes around 3:00 AM the morning of Monday, May 8. As the FCC analyzed the log files, it became clear that non-human bots created these comments automatically by making calls to the FCC’s API. Interestingly, the attack did not come from a botnet of infected computers but was fully cloud-based. By using commercial cloud services to make massive API requests, the bots consumed available machine resources, which crowded out human commenters. In effect, the bot swarm created a distributed denial-of-service attack on FCC systems using the public API as a vehicle. It’s similar to the distributed denial of service attack on Pokemon Go in July 2016. This description “sounds like a ‘Layer 7’ or Application Layer attack,” Cloudflare Information Security Chief Marc Rogers told Ars. This is a type of DDoS, although it’s different from the ones websites are normally hit with. “In this type of [DDoS] attack, instead of trying to saturate the site’s network by flooding it with junk traffic, the attacker instead tries to bring a site down by attacking an application running on it,” Rogers said. “I am a little surprised that people are challenging the FCC’s decision to call this a DDoS,” Rogers also said. Cloudflare operates a global network that improves performance of websites and protects them from DDoS attacks and other security threats. When asked if the FCC still believes it was hit with DDoS attacks, an FCC spokesperson told Ars that “there have been DDoS attacks during this process,” including the morning of May 8. But the FCC official we talked to offered a bit less certainty on that point. “The challenge is someone trying to deny service would do the same thing as someone who just doesn’t know how to write a bot well,” the FCC official said. FCC officials said they spoke with law enforcement about the incident. Spam bots and DDoS could have same effect DDoS attacks, according to CDN provider Akamai, “are malicious attempts to render a website or Web application unavailable to users by overwhelming the site with an enormous amount of traffic, causing the site to crash or operate very slowly.” DDoS attacks are “distributed” because the attacks generally “use large armies of automated ‘bots’—computers that have been infected with malware and can be remotely controlled by hackers.” (Akamai declined to comment on the FCC downtime when contacted by Ars.) In this case, the FCC’s media spokesperson told Ars the traffic did not come from infected computers. Instead, the traffic came from “cloud-based bots which made it harder to implement usual DDoS defenses.” The FCC official involved in the DDoS response told us that the comment system “experienced a large number of non-human digital queries,” but that “the number of automated comments being submitted was much less than other API calls, raising questions as to their purpose.” If these were simply spammers who wanted to flood the FCC with as many comments as possible, like those who try to artificially inflate the number of either pro- or anti-net neutrality comments, they could have used the system’s bulk filing mechanism instead of the API. But the suspicious traffic came through the API, and the API queries were “malformed.” This means that “they aren’t formatted well—they either don’t fit the normal API spec or they are designed in such a way that they excessively tax the system when a simpler call could be done,” the FCC official said. Whether May 8 was the work of spam bots or DDoS attackers, “the effect would have been the same—denial of service to human users” who were trying to submit comments, the FCC official said. But these bots were submitting many fewer comments than other entities making API calls, suggesting that, if they were spam bots, they were “very poorly written.” The official said a similar event happened in 2014 during the previous debate over net neutrality rules, when bots tied up the system by filing comments and then immediately searching for them. “One has to ask why a bot would file, search, file, search, over and over,” the official said. If it was just a spam bot, “one has to wonder why, if the outside entity really wanted to upload lots of comments in bulk, they didn’t use the alternative bulk file upload mechanism” and “why the bots were submitting a much lower number of comments relative to other API calls,” the official said. The FCC says it stopped the attacks by 8:45am ET on May 8, but the days that followed were still plagued by intermittent downtime. “There were other waves after 8:45am that slowed the system for some and, as noted, there were ‘bots’ plural, not just one,” the FCC official said. On May 10, “we saw other attempts where massive malformed search queries also have hit the system, though it is unclear if the requestors meant for them to be poorly formed or not. The IT team has implemented solutions to handle them even if the API requests were malformed.” Was it a DDoS, or did it just look like one? There is some history of attackers launching DDoS attacks from public cloud services like Amazon’s. But the kind of traffic coming into the FCC after the John Oliver show might have looked like DDoS traffic even if it wasn’t, security company Arbor Networks says. Arbor Networks, which sells DDoS protection products, offered some analysis for its customers and shared the analysis with Ars yesterday. Arbor says: When a client has an active connection to a website which is under heavy load, there is a risk that the server will be unable to respond in a timely fashion. The client will then start to automatically resend its data, causing increased load. After a while, the user will also get impatient and will start to refresh the screen and repeatedly press the “Submit” button, increasing the load even further. Finally, the user will, in most cases, close the browser session and will attempt to reconnect to the website. This will then generate TCP SYN packets which, if processed correctly, will move to the establishment of the SSL session which involves key generation, key exchange, and other compute intensive processes. This will most likely also timeout, leaving sessions hanging and resulting in resource starvation on the server. A spam bot would behave in the same manner, “attempting to re-establish its sessions, increasing the load even further,” Arbor says. “Also, if the bot author wasn’t careful with his error handling code, the bot might also have become very aggressive and start to flood the server with additional requests.” What the FCC saw in this type of situation might have looked like a DDoS attack regardless of whether it was one, Arbor said: When viewed from the network level, there will be a flood of TCP SYN packets from legitimate clients attempting to connect; there will be a number of half-open SSL session which are attempting to finalize the setup phase and a large flood of application packets from clients attempting to send data to the Web server. Taken together, this will, in many ways, look similar to a multi-faceted DDoS attack using a mix of TCP-SYN flooding, SSL key exchange starvation, and HTTP/S payload attacks. This traffic can easily be mistaken for a DDoS attack when, in fact, it is the result of a flash crowd and spam bot all attempting to post responses to a website in the same time period. DDoS attacks generally try to “saturate all of the bandwidth that the target has available,” Fastly CTO Tyler McMullen told Ars. (Fastly provides cloud security and other Web performance tools.) In the FCC’s case, the attack sounds like it came from a small number of machines on a public cloud, he said. “Another form of denial-of-service attack is to make requests of a service that are computationally expensive,” he said. “By doing this, you don’t need a ton of infected devices to bring down a site—if the service is not protected against this kind of attack, it often doesn’t take much to take it offline. The amount of traffic referenced here does not make it obvious that it was a DDoS [against the FCC].” Server logs remain secret The FCC declined to publicly release server logs because they might contain private information such as IP addresses, according to ZDNet. The logs reportedly contain about 1GB of data per hour from the time period in question, which lasted nearly eight hours. The privacy concerns are legitimate, security experts told Ars. “Releasing the raw logs from their platform would almost certainly harm user privacy,” Rogers of Cloudflare told Ars. “Finally, redacting the logs would not be a simple task. The very nature of application layer attacks is to look exactly like legitimate user traffic.” McMullen agreed. “Releasing the logs publicly would definitely allow [the details of the attack] to be confirmed, but the risk of revealing personal information here is real,” he said. “IP addresses can sometimes be tied to an individual user. Worse, an IP address combined with the time at which the request occurred can make the individual user’s identity even more obvious.” But there are ways to partially redact IP addresses so that they cannot be tied to an individual, he said. “One could translate the IP addresses into their AS numbers, which is roughly the equivalent of replacing a specific street address with the name of the state the address is in,” he said. “That said, this would still make it clear whether the traffic was coming from a network used by humans (e.g. Comcast, Verizon, AT&T, etc) or one that primarily hosts servers.” Open by design The FCC’s public comments system is supposed to allow anyone to submit a comment, which raises some challenges in trying to prevent large swarms of traffic that can take down the site. The FCC has substantially upgraded its website and the back-end systems that support it since the 2014 net neutrality debate. Instead of ancient in-house servers, the comment system is now hosted on the Amazon cloud, which IT departments can use to scale computing resources up and down as needed. But this month’s events show that more work needs to be done. The FCC had already implemented a rate limit on its API, but the limit “is tied to a key, and, if bots requested multiple keys, they could bypass the limit,” the FCC official told us. The FCC has avoided using CAPTCHA systems to distinguish bots from humans because of “challenges to individuals who have different visual or other needs,” the official said. Even “NoCAPTCHA” systems that only require users to click a box instead of entering a hard-to-read string of characters can be problematic. “Some stakeholders who are both visually impaired and hearing impaired have reported browser issues with NoCAPTCHA,” the FCC official said. “Also a NoCAPTCHA would mean you would have to turn off the API,” but there are groups who want to use the API to submit comments on behalf of others in an automated fashion. Comments are often submitted in bulk both by pro- and anti-net neutrality groups. The FCC said it worked with its cloud partners to stop the most recent attacks, but it declined to share more details on what changes were made. “If folks knew everything we did, they could possibly work around what we did,” the FCC official said. Senate Democrats asked the FCC to provide details on how it will prevent future attacks. While the net neutrality record now contains many comments of questionable origin and quality, the FCC apparently won’t be throwing any of them out. But that doesn’t mean they’ll hold any weight on the decision-making process. “What matters most are the quality of the comments, not the quantity,” Pai said at a press conference this month. “Obviously, fake comments such as the ones submitted last week by the Flash, Batman, Wonder Woman, Aquaman, and Superman are not going to dramatically impact our deliberations on this issue.” There is “a tension between having open process where it’s easy to comment and preventing questionable comments from being filed,” Pai said. “Generally speaking, this agency has erred on the side of openness. We want to encourage people to participate in as easy and accessible a way as possible.” Source: https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2017/05/examining-the-fcc-claim-that-ddos-attacks-hit-net-neutrality-comment-system/
Excerpt from:
Examining the FCC claim that DDoS attacks hit net neutrality comment system
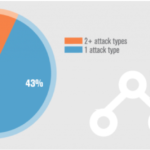 Information security company Verisign just published its Distributed Denial of Trends Report for Q1 2017. This report talks about changes in the frequency, size, and type of DDoS attack that the company has observed over the first few months of this year. The main takeaway is this: The number of DDoS attacks has plunged by 23 percent compared to the previous quarter. That’s good! However, the average peak attack size has increased by almost 26 percent, making them vastly more potent at taking down websites and critical online infrastructure. That’s bad. The report also notes that attacks are sophisticated in nature, and use several different attack types to take down a website. While 43 percent use just one attack vector, 25 percent use two, and six percent use five. This, obviously, makes it much more difficult to mitigate against. Verisign’s report also talks about the largest DDoS attack observed by the company in Q1. This was a multi-vector attack that peaked at 120 Gbps, and with a throughput of 90 Mpps. Per the report: This attack sent a flood of traffic to the targeted network in excess of 60 Gbps for more than 15 hours. The attackers were very persistent in their attempts to disrupt the victim’s network by sending attack traffic on a daily basis for over two weeks. The attack consisted primarily of TCP SYN and TCP RST floods of varying packet sizes and employed one of the signatures associated with the Mirai IoT botnet. The event also included UDP floods and IP fragments which increased the volume of the attack. So, in short. The attackers were using several different attack types, and they were able to sustain the attack over a long period of time. This shows the attacker has resources, either to create or rent a botnet of that size, and to sustain an attack over two weeks. The fact that DDoS attacks have increased in potency is hardly a surprise. They’ve been getting bigger and bigger, as bad actors figure out they can easily rope insecure Internet of Things (IoT) devices into their botnets. The Mirai botnet, for example, which took down Dyn last year, and with it much of the Internet, consisted of hundreds of thousands of insecure IoT products. The main thing you can gleam from the Verisign report is that DDoS attacks are increasingly professional, for lack of a better word. It’s not 2005 anymore. We’ve moved past the halcyon days of teenagers taking down sites with copies of LOIC they’d downloaded off Rapidshare. Now, it’s more potent. More commoditized. And the people operating them aren’t doing it for shits and giggles. Source: https://thenextweb.com/insider/2017/05/24/report-ddos-attacks-are-less-common-but-theyre-bigger/#.tnw_RJHfi1AZ
Information security company Verisign just published its Distributed Denial of Trends Report for Q1 2017. This report talks about changes in the frequency, size, and type of DDoS attack that the company has observed over the first few months of this year. The main takeaway is this: The number of DDoS attacks has plunged by 23 percent compared to the previous quarter. That’s good! However, the average peak attack size has increased by almost 26 percent, making them vastly more potent at taking down websites and critical online infrastructure. That’s bad. The report also notes that attacks are sophisticated in nature, and use several different attack types to take down a website. While 43 percent use just one attack vector, 25 percent use two, and six percent use five. This, obviously, makes it much more difficult to mitigate against. Verisign’s report also talks about the largest DDoS attack observed by the company in Q1. This was a multi-vector attack that peaked at 120 Gbps, and with a throughput of 90 Mpps. Per the report: This attack sent a flood of traffic to the targeted network in excess of 60 Gbps for more than 15 hours. The attackers were very persistent in their attempts to disrupt the victim’s network by sending attack traffic on a daily basis for over two weeks. The attack consisted primarily of TCP SYN and TCP RST floods of varying packet sizes and employed one of the signatures associated with the Mirai IoT botnet. The event also included UDP floods and IP fragments which increased the volume of the attack. So, in short. The attackers were using several different attack types, and they were able to sustain the attack over a long period of time. This shows the attacker has resources, either to create or rent a botnet of that size, and to sustain an attack over two weeks. The fact that DDoS attacks have increased in potency is hardly a surprise. They’ve been getting bigger and bigger, as bad actors figure out they can easily rope insecure Internet of Things (IoT) devices into their botnets. The Mirai botnet, for example, which took down Dyn last year, and with it much of the Internet, consisted of hundreds of thousands of insecure IoT products. The main thing you can gleam from the Verisign report is that DDoS attacks are increasingly professional, for lack of a better word. It’s not 2005 anymore. We’ve moved past the halcyon days of teenagers taking down sites with copies of LOIC they’d downloaded off Rapidshare. Now, it’s more potent. More commoditized. And the people operating them aren’t doing it for shits and giggles. Source: https://thenextweb.com/insider/2017/05/24/report-ddos-attacks-are-less-common-but-theyre-bigger/#.tnw_RJHfi1AZ 


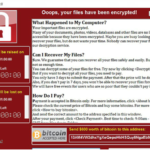 What is it ? WannaCry also know as WanaCrypt 2.0 is a form of malware commonly known as “Ransom Ware”. Where did it come from ? It was originally developed by the NSA in the US called “Eternal Blue” and was a way for them to secretly access computers. It was based on a flaw in windows machines, Unfortunately the NSA did not store this weaponized malware securely enough and someone hacked in and stole it. At this point it was loose and easily findable on the Internet. If you see a screen like this, you’re machine is definitely infected. Here is a link below from Microsoft to check/scan if your PC has a virus. https://www.microsoft.com/security/scanner/en-us/default.aspx Who is responsible for this ? At this point no one knows but there are a lot of smart people working on it and they will be caught eventually…This is my opinion. Is someone making money from this ? Yes, as with all ransom ware there is a money component.These are 3 discovered bitcoin Identifiers that victims are paying the ransom to Which is hardcoded into the Malware. As of 09:15 EST May 14, 2017 The total ransom paid is a total of $15,150.00 USD. This is surprisingly low, it’s definitely going to rise. Check for yourself on its progress by clicking the 3 links below. https://blockchain.info/address/13AM4VW2dhxYgXeQepoHkHSQuy6NgaEb94 https://blockchain.info/address/12t9YDPgwueZ9NyMgw519p7AA8isjr6SMw https://blockchain.info/address/115p7UMMngoj1pMvkpHijcRdfJNXj6LrLn How did my computer get infected ? If you’re on a corporate network, you most likely got it from another computer on your network. If you’re at home on a cable modem you got it through email phishing or visiting a hacked or a sketchy website. How did it spread so quickly ? As you most likely know by now, millions of computers were infected in a few short days and those most affected by this are on corporate, Government and University networks. It spreads on these networks by using a windows flaw that goes from machine to machine using Microsoft’s SMB feature . Here’s a short list of victims from GITHUB NHS (uk) turning away patients, unable to perform x-rays. (list of affected hospitals) Nissan (uk) http://www.chroniclelive.co.uk/news/north-east-news/cyber-attack-nhs-latest-news-13029913 Telefonica (spain) ( https://twitter.com/SkyNews/status/863044193727389696 ) power firm Iberdrola and Gas Natural ( spain ) FedEx (us) ( https://twitter.com/jeancreed1/status/863089728253505539 ) University of Waterloo ( us ) Russia interior ministry & Megafon (russia) https://twitter.com/dabazdyrev/status/863034199460261890/photo/1 VTB (russian bank) https://twitter.com/vassgatov/status/863175506790952962 Russian Railroads (RZD) https://twitter.com/vassgatov/status/863175723846176768 Portugal Telecom ???????? – Sberbank Russia ( russia ) Shaheen Airlines (india, claimed on twitter) Train station in frankfurt ( germany ) Neustadt station ( germany ) the entire network of German Rail seems to be affected ( @farbenstau ) in China secondary schools and universities had been affected ( source ) A Library in Oman ( @99arwan1 ) China Yanshui County Public Security Bureau ( https://twitter.com/95cnsec/status/863292545278685184 ) Schools/Education (France) https://twitter.com/Damien_Bancal/status/863305670568837120 A mall in singapore https://twitter.com/nkl0x55/status/863340271391580 ATMs in china https://twitter.com/95cnsec/status/863382193615159 Renault STC telecom Norwegian soccer team ticket sales Is my website spreading this malware ? I can only say that any DOSarrest customers using our advanced WAF are not spreading this Malware as we won’t allow this type of malicious traffic to get to your server. Is it still spreading ? No, good news ! This thing had a kill switch built into its code, so if any machine can access this site www.iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea.com it won’t spread from that machine. I’m infected, What should I do ? We recommend that you wipe your machine clean and restore from back-ups….of course everyone has backups, Right ? Need more info… Try Github.com Microsoft to get the free patch if you need it. Source: https://www.dosarrest.com/ddos-blog/wannacry-faq/
What is it ? WannaCry also know as WanaCrypt 2.0 is a form of malware commonly known as “Ransom Ware”. Where did it come from ? It was originally developed by the NSA in the US called “Eternal Blue” and was a way for them to secretly access computers. It was based on a flaw in windows machines, Unfortunately the NSA did not store this weaponized malware securely enough and someone hacked in and stole it. At this point it was loose and easily findable on the Internet. If you see a screen like this, you’re machine is definitely infected. Here is a link below from Microsoft to check/scan if your PC has a virus. https://www.microsoft.com/security/scanner/en-us/default.aspx Who is responsible for this ? At this point no one knows but there are a lot of smart people working on it and they will be caught eventually…This is my opinion. Is someone making money from this ? Yes, as with all ransom ware there is a money component.These are 3 discovered bitcoin Identifiers that victims are paying the ransom to Which is hardcoded into the Malware. As of 09:15 EST May 14, 2017 The total ransom paid is a total of $15,150.00 USD. This is surprisingly low, it’s definitely going to rise. Check for yourself on its progress by clicking the 3 links below. https://blockchain.info/address/13AM4VW2dhxYgXeQepoHkHSQuy6NgaEb94 https://blockchain.info/address/12t9YDPgwueZ9NyMgw519p7AA8isjr6SMw https://blockchain.info/address/115p7UMMngoj1pMvkpHijcRdfJNXj6LrLn How did my computer get infected ? If you’re on a corporate network, you most likely got it from another computer on your network. If you’re at home on a cable modem you got it through email phishing or visiting a hacked or a sketchy website. How did it spread so quickly ? As you most likely know by now, millions of computers were infected in a few short days and those most affected by this are on corporate, Government and University networks. It spreads on these networks by using a windows flaw that goes from machine to machine using Microsoft’s SMB feature . Here’s a short list of victims from GITHUB NHS (uk) turning away patients, unable to perform x-rays. (list of affected hospitals) Nissan (uk) http://www.chroniclelive.co.uk/news/north-east-news/cyber-attack-nhs-latest-news-13029913 Telefonica (spain) ( https://twitter.com/SkyNews/status/863044193727389696 ) power firm Iberdrola and Gas Natural ( spain ) FedEx (us) ( https://twitter.com/jeancreed1/status/863089728253505539 ) University of Waterloo ( us ) Russia interior ministry & Megafon (russia) https://twitter.com/dabazdyrev/status/863034199460261890/photo/1 VTB (russian bank) https://twitter.com/vassgatov/status/863175506790952962 Russian Railroads (RZD) https://twitter.com/vassgatov/status/863175723846176768 Portugal Telecom ???????? – Sberbank Russia ( russia ) Shaheen Airlines (india, claimed on twitter) Train station in frankfurt ( germany ) Neustadt station ( germany ) the entire network of German Rail seems to be affected ( @farbenstau ) in China secondary schools and universities had been affected ( source ) A Library in Oman ( @99arwan1 ) China Yanshui County Public Security Bureau ( https://twitter.com/95cnsec/status/863292545278685184 ) Schools/Education (France) https://twitter.com/Damien_Bancal/status/863305670568837120 A mall in singapore https://twitter.com/nkl0x55/status/863340271391580 ATMs in china https://twitter.com/95cnsec/status/863382193615159 Renault STC telecom Norwegian soccer team ticket sales Is my website spreading this malware ? I can only say that any DOSarrest customers using our advanced WAF are not spreading this Malware as we won’t allow this type of malicious traffic to get to your server. Is it still spreading ? No, good news ! This thing had a kill switch built into its code, so if any machine can access this site www.iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea.com it won’t spread from that machine. I’m infected, What should I do ? We recommend that you wipe your machine clean and restore from back-ups….of course everyone has backups, Right ? Need more info… Try Github.com Microsoft to get the free patch if you need it. Source: https://www.dosarrest.com/ddos-blog/wannacry-faq/