New vulnerability in DNS server software can be leveraged for DDoS attacks with an 1620x amplification factor. A team of academics from Israel has disclosed today details about NXNSAttack, a vulnerability in DNS servers that can be abused to launch DDoS attacks of massive proportions. According to the research team, NXNSAttack impacts recursive DNS servers and the process of DNS delegation. Recursive DNS servers are DNS systems that pass DNS queries upstream in order to be resolved and converted from a domain name into an IP address. These conversions take place on authoritative DNS servers, the servers that contain a copy of the DNS record, and are authorized to resolve it. However, as a safety mechanism part of the DNS protocol, authoritative DNS servers can also “delegate” this operation to alternative DNS servers of their choosing. New NXNSAttack explained In a research paper published today, academics from the Tel Aviv University and The Interdisciplinary Center in Herzliya, Israel, said they found a way to abuse this delegation process for DDoS attacks. The NXNSAttack technique has different facets and variations, but the basic steps are detailed below: 1) An attacker sends a DNS query to a recursive DNS server. The request is for a domain like “attacker.com,” which is managed through an attacker-controlled authoritative DNS server. 2) Since the recursive DNS server is not authorized to resolve this domain, it forwards the operation to the attacker’s malicious authoritative DNS server. 3) The malicious DNS server replies to the recursive DNS server with a message that equates to “I’m delegating this DNS resolving operation to this large list of name servers.” The list contains thousands of subdomains for a victim website. 4) The recursive DNS server forwards the DNS query to all the subdomains on the list, creating a surge in traffic for the victim’s authoritative DNS server. Image: NIC.CZ NXNSAttack has a huge amplification factor The research team says that an attacker using NXNSAttack can amplify a simple DNS query from 2 to 1,620 times its initial size, creating a massive spike in traffic that can crash a victim’s DNS server. Once the DNS server goes down, this also prevents users from accessing the attacked website, as the site’s domain can’t be resolved anymore. The research team says the NXNSAttack packet amplification factor (PAF) depends on the DNS software running on a recursive DNS server; however, in most cases, the amplification factor is many times larger than other DDoS amplification (reflection) attacks, where the PAF is usually between lowly values of 2 and 10. This large PAF implies that NXNSAttack is one of the most dangerous DDoS attack vectors known to date, having the ability to launch debilitating attacks with only a few devices and automated DNS queries. Patches available for DNS software The Israeli researchers said they’ve been working for the past few months with the makers of DNS software, content delivery networks, and managed DNS providers to apply mitigations to DNS servers across the world. Impacted software includes the likes of ISC BIND (CVE-2020-8616), NLnet labs Unbound (CVE-2020-12662), PowerDNS (CVE-2020-10995), and CZ.NIC Knot Resolver (CVE-2020-12667), but also commercial DNS services provided by companies like Cloudflare, Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Oracle (DYN), Verisign, IBM Quad9, and ICANN. Image: Shafir et al. Patches have been released today and over the previous weeks. They include mitigations that prevent attackers from abusing the DNS delegation process to flood other DNS servers. Server administrators who run their own DNS servers are advised to update DNS resolver software to the latest version. The research team’s work has been detailed in an academic paper entitled “ NXNSAttack: Recursive DNS Inefficiencies and Vulnerabilities ,” available for download in PDF format . Source: https://www.zdnet.com/article/nxnsattack-technique-can-be-abused-for-large-scale-ddos-attacks/
View the original here:
NXNSAttack technique can be abused for large-scale DDoS attacks


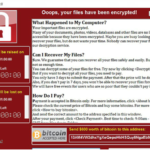 What is it ? WannaCry also know as WanaCrypt 2.0 is a form of malware commonly known as “Ransom Ware”. Where did it come from ? It was originally developed by the NSA in the US called “Eternal Blue” and was a way for them to secretly access computers. It was based on a flaw in windows machines, Unfortunately the NSA did not store this weaponized malware securely enough and someone hacked in and stole it. At this point it was loose and easily findable on the Internet. If you see a screen like this, you’re machine is definitely infected. Here is a link below from Microsoft to check/scan if your PC has a virus. https://www.microsoft.com/security/scanner/en-us/default.aspx Who is responsible for this ? At this point no one knows but there are a lot of smart people working on it and they will be caught eventually…This is my opinion. Is someone making money from this ? Yes, as with all ransom ware there is a money component.These are 3 discovered bitcoin Identifiers that victims are paying the ransom to Which is hardcoded into the Malware. As of 09:15 EST May 14, 2017 The total ransom paid is a total of $15,150.00 USD. This is surprisingly low, it’s definitely going to rise. Check for yourself on its progress by clicking the 3 links below. https://blockchain.info/address/13AM4VW2dhxYgXeQepoHkHSQuy6NgaEb94 https://blockchain.info/address/12t9YDPgwueZ9NyMgw519p7AA8isjr6SMw https://blockchain.info/address/115p7UMMngoj1pMvkpHijcRdfJNXj6LrLn How did my computer get infected ? If you’re on a corporate network, you most likely got it from another computer on your network. If you’re at home on a cable modem you got it through email phishing or visiting a hacked or a sketchy website. How did it spread so quickly ? As you most likely know by now, millions of computers were infected in a few short days and those most affected by this are on corporate, Government and University networks. It spreads on these networks by using a windows flaw that goes from machine to machine using Microsoft’s SMB feature . Here’s a short list of victims from GITHUB NHS (uk) turning away patients, unable to perform x-rays. (list of affected hospitals) Nissan (uk) http://www.chroniclelive.co.uk/news/north-east-news/cyber-attack-nhs-latest-news-13029913 Telefonica (spain) ( https://twitter.com/SkyNews/status/863044193727389696 ) power firm Iberdrola and Gas Natural ( spain ) FedEx (us) ( https://twitter.com/jeancreed1/status/863089728253505539 ) University of Waterloo ( us ) Russia interior ministry & Megafon (russia) https://twitter.com/dabazdyrev/status/863034199460261890/photo/1 VTB (russian bank) https://twitter.com/vassgatov/status/863175506790952962 Russian Railroads (RZD) https://twitter.com/vassgatov/status/863175723846176768 Portugal Telecom ???????? – Sberbank Russia ( russia ) Shaheen Airlines (india, claimed on twitter) Train station in frankfurt ( germany ) Neustadt station ( germany ) the entire network of German Rail seems to be affected ( @farbenstau ) in China secondary schools and universities had been affected ( source ) A Library in Oman ( @99arwan1 ) China Yanshui County Public Security Bureau ( https://twitter.com/95cnsec/status/863292545278685184 ) Schools/Education (France) https://twitter.com/Damien_Bancal/status/863305670568837120 A mall in singapore https://twitter.com/nkl0x55/status/863340271391580 ATMs in china https://twitter.com/95cnsec/status/863382193615159 Renault STC telecom Norwegian soccer team ticket sales Is my website spreading this malware ? I can only say that any DOSarrest customers using our advanced WAF are not spreading this Malware as we won’t allow this type of malicious traffic to get to your server. Is it still spreading ? No, good news ! This thing had a kill switch built into its code, so if any machine can access this site www.iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea.com it won’t spread from that machine. I’m infected, What should I do ? We recommend that you wipe your machine clean and restore from back-ups….of course everyone has backups, Right ? Need more info… Try Github.com Microsoft to get the free patch if you need it. Source: https://www.dosarrest.com/ddos-blog/wannacry-faq/
What is it ? WannaCry also know as WanaCrypt 2.0 is a form of malware commonly known as “Ransom Ware”. Where did it come from ? It was originally developed by the NSA in the US called “Eternal Blue” and was a way for them to secretly access computers. It was based on a flaw in windows machines, Unfortunately the NSA did not store this weaponized malware securely enough and someone hacked in and stole it. At this point it was loose and easily findable on the Internet. If you see a screen like this, you’re machine is definitely infected. Here is a link below from Microsoft to check/scan if your PC has a virus. https://www.microsoft.com/security/scanner/en-us/default.aspx Who is responsible for this ? At this point no one knows but there are a lot of smart people working on it and they will be caught eventually…This is my opinion. Is someone making money from this ? Yes, as with all ransom ware there is a money component.These are 3 discovered bitcoin Identifiers that victims are paying the ransom to Which is hardcoded into the Malware. As of 09:15 EST May 14, 2017 The total ransom paid is a total of $15,150.00 USD. This is surprisingly low, it’s definitely going to rise. Check for yourself on its progress by clicking the 3 links below. https://blockchain.info/address/13AM4VW2dhxYgXeQepoHkHSQuy6NgaEb94 https://blockchain.info/address/12t9YDPgwueZ9NyMgw519p7AA8isjr6SMw https://blockchain.info/address/115p7UMMngoj1pMvkpHijcRdfJNXj6LrLn How did my computer get infected ? If you’re on a corporate network, you most likely got it from another computer on your network. If you’re at home on a cable modem you got it through email phishing or visiting a hacked or a sketchy website. How did it spread so quickly ? As you most likely know by now, millions of computers were infected in a few short days and those most affected by this are on corporate, Government and University networks. It spreads on these networks by using a windows flaw that goes from machine to machine using Microsoft’s SMB feature . Here’s a short list of victims from GITHUB NHS (uk) turning away patients, unable to perform x-rays. (list of affected hospitals) Nissan (uk) http://www.chroniclelive.co.uk/news/north-east-news/cyber-attack-nhs-latest-news-13029913 Telefonica (spain) ( https://twitter.com/SkyNews/status/863044193727389696 ) power firm Iberdrola and Gas Natural ( spain ) FedEx (us) ( https://twitter.com/jeancreed1/status/863089728253505539 ) University of Waterloo ( us ) Russia interior ministry & Megafon (russia) https://twitter.com/dabazdyrev/status/863034199460261890/photo/1 VTB (russian bank) https://twitter.com/vassgatov/status/863175506790952962 Russian Railroads (RZD) https://twitter.com/vassgatov/status/863175723846176768 Portugal Telecom ???????? – Sberbank Russia ( russia ) Shaheen Airlines (india, claimed on twitter) Train station in frankfurt ( germany ) Neustadt station ( germany ) the entire network of German Rail seems to be affected ( @farbenstau ) in China secondary schools and universities had been affected ( source ) A Library in Oman ( @99arwan1 ) China Yanshui County Public Security Bureau ( https://twitter.com/95cnsec/status/863292545278685184 ) Schools/Education (France) https://twitter.com/Damien_Bancal/status/863305670568837120 A mall in singapore https://twitter.com/nkl0x55/status/863340271391580 ATMs in china https://twitter.com/95cnsec/status/863382193615159 Renault STC telecom Norwegian soccer team ticket sales Is my website spreading this malware ? I can only say that any DOSarrest customers using our advanced WAF are not spreading this Malware as we won’t allow this type of malicious traffic to get to your server. Is it still spreading ? No, good news ! This thing had a kill switch built into its code, so if any machine can access this site www.iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea.com it won’t spread from that machine. I’m infected, What should I do ? We recommend that you wipe your machine clean and restore from back-ups….of course everyone has backups, Right ? Need more info… Try Github.com Microsoft to get the free patch if you need it. Source: https://www.dosarrest.com/ddos-blog/wannacry-faq/ 
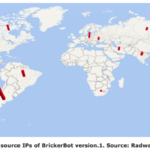 Canada is among the countries that have been stung by a mysterious botnet infecting Internet-connected devices using the Linux and BusyBox operating systems that essentially trashes the hardware, according to a security vendor. Called a Permanent Denial of Service attack (PDoS) – also called “plashing” by some – the attack exploits security flaws or misconfiguration and goes on to destroy device firmware and/or basic functions of a system, Radware said in a blog released last week. The first of two versions has rendered IoT devices affected into bricks, which presumably is why the attack has been dubbed the BrickerBot. A second version goes after IoT devices and Linux servers. “Over a four-day period, Radware’s honeypot recorded 1,895 PDoS attempts performed from several locations around the world,” the company said in the blog. “Its sole purpose was to compromise IoT devices and corrupt their storage.” After accessing a device by brute force attacks on the Telnet login, the malware issues a series of Linux commands that will lead to corrupted storage, followed by commands to disrupt Internet connectivity, device performance, and the wiping of all files on the device. Vulnerable devices have their Telnet port open. Devices tricked into spreading the attack — mainly equipment from Ubiquiti Networks Inc. including wireless access points and bridges with beam directivity — ran an older version of the Dropbear secure shell (SSH) server. Radware estimates there are over 20 million devices with Dropbear connected to the Internet now which could be leveraged for attacks. Targets include digital video cameras and recorders, which have also been victimized by the Mirai or similar IoT botnets. According to Radware, the PDoS attempts it detected came from a limited number of IP addresses in Argentina, the U.S., Canada, Russia, Iran, India, South Africa and other countries. Two versions of the bot were found starting March 20: Version one, which was short-lived and aimed at BusyBox devices, and version two, which continues and has a wider number of targets. While the IP addresses of servers used to launch the first attack can be mapped, the more random addresses of servers used in the second attack have been obscured by Tor egress nodes. The second version is not only going after IoT devices but also Unix and Linux servers by adding new commands. What makes this botnet mysterious is that it wipes out devices, rather than try to assemble them into a large dagger that can knock out web sites – like Mirai. “BrickerBot 2 is still ongoing,” Pascal Geenens, a Radware security evangelist based in Belgium, said in a phone interview this morning. “We still don’t have an idea who it is because it’s still hiding behind the Tor network.” “We still have a lot of questions like where was it originating from, what is the motivation? One of them could be someone who’s angry at IoT manufacturers for not solving that [security] problem, maybe somebody who suffered a DDoS attack and wants to get back at manufacturers by bricking the devices. That way it solves the IoT problem and gets back at manufacturers. “Another idea that I have is maybe its a hacker that is running Windows-based botnets, which are more costly to maintain.” It’s easy to inspect and compromise an IoT device through a Telnet command, he explained, so IoT botnet are easy to assemble. That lowers the cost for a botnet-for-hire. By comparison Windows devices have to be compromised through phishing campaigns that trick end users into downloading binaries that evade anti-virus software. It’s complex. So Geenens wonders if a hacker’s goal here is to get into IoT botnets and destroy the devices, which then raises the value of his Windows botnet. Another theory is the attacker is searching for Linux-based honeypots — traps set by infosec pros — with default passwords. He also pointed out Unix or Linux-based servers with default credentials are vulnerable to the BrickerBot 2 attack. However, he added, there wouldn’t be many of those because during installation process Linux ask for creation of a root password, so there isn’t a default credential. The exception, he added, is a pre-installed image downloaded from the Internet. Administrators who have these devices on their networks are urged to change factory default credentials and disable Telnet access. Network and user behavior analysis can detect anomalies in traffic, says Radware. Source: http://www.itworldcanada.com/article/canada-one-of-sources-for-destructive-iot-botnet/392242
Canada is among the countries that have been stung by a mysterious botnet infecting Internet-connected devices using the Linux and BusyBox operating systems that essentially trashes the hardware, according to a security vendor. Called a Permanent Denial of Service attack (PDoS) – also called “plashing” by some – the attack exploits security flaws or misconfiguration and goes on to destroy device firmware and/or basic functions of a system, Radware said in a blog released last week. The first of two versions has rendered IoT devices affected into bricks, which presumably is why the attack has been dubbed the BrickerBot. A second version goes after IoT devices and Linux servers. “Over a four-day period, Radware’s honeypot recorded 1,895 PDoS attempts performed from several locations around the world,” the company said in the blog. “Its sole purpose was to compromise IoT devices and corrupt their storage.” After accessing a device by brute force attacks on the Telnet login, the malware issues a series of Linux commands that will lead to corrupted storage, followed by commands to disrupt Internet connectivity, device performance, and the wiping of all files on the device. Vulnerable devices have their Telnet port open. Devices tricked into spreading the attack — mainly equipment from Ubiquiti Networks Inc. including wireless access points and bridges with beam directivity — ran an older version of the Dropbear secure shell (SSH) server. Radware estimates there are over 20 million devices with Dropbear connected to the Internet now which could be leveraged for attacks. Targets include digital video cameras and recorders, which have also been victimized by the Mirai or similar IoT botnets. According to Radware, the PDoS attempts it detected came from a limited number of IP addresses in Argentina, the U.S., Canada, Russia, Iran, India, South Africa and other countries. Two versions of the bot were found starting March 20: Version one, which was short-lived and aimed at BusyBox devices, and version two, which continues and has a wider number of targets. While the IP addresses of servers used to launch the first attack can be mapped, the more random addresses of servers used in the second attack have been obscured by Tor egress nodes. The second version is not only going after IoT devices but also Unix and Linux servers by adding new commands. What makes this botnet mysterious is that it wipes out devices, rather than try to assemble them into a large dagger that can knock out web sites – like Mirai. “BrickerBot 2 is still ongoing,” Pascal Geenens, a Radware security evangelist based in Belgium, said in a phone interview this morning. “We still don’t have an idea who it is because it’s still hiding behind the Tor network.” “We still have a lot of questions like where was it originating from, what is the motivation? One of them could be someone who’s angry at IoT manufacturers for not solving that [security] problem, maybe somebody who suffered a DDoS attack and wants to get back at manufacturers by bricking the devices. That way it solves the IoT problem and gets back at manufacturers. “Another idea that I have is maybe its a hacker that is running Windows-based botnets, which are more costly to maintain.” It’s easy to inspect and compromise an IoT device through a Telnet command, he explained, so IoT botnet are easy to assemble. That lowers the cost for a botnet-for-hire. By comparison Windows devices have to be compromised through phishing campaigns that trick end users into downloading binaries that evade anti-virus software. It’s complex. So Geenens wonders if a hacker’s goal here is to get into IoT botnets and destroy the devices, which then raises the value of his Windows botnet. Another theory is the attacker is searching for Linux-based honeypots — traps set by infosec pros — with default passwords. He also pointed out Unix or Linux-based servers with default credentials are vulnerable to the BrickerBot 2 attack. However, he added, there wouldn’t be many of those because during installation process Linux ask for creation of a root password, so there isn’t a default credential. The exception, he added, is a pre-installed image downloaded from the Internet. Administrators who have these devices on their networks are urged to change factory default credentials and disable Telnet access. Network and user behavior analysis can detect anomalies in traffic, says Radware. Source: http://www.itworldcanada.com/article/canada-one-of-sources-for-destructive-iot-botnet/392242