The cloud offers organizations a number of benefits, from simple off-site storage to rent-a-server to complete services. But 2017 will also see cloud infrastructure increasingly the target of attacks, with criminals lured by the data stored there and the possibility of using it to launch distributed denial of service attacks. That’s one of the predictions for the new year from security vendor Forcepoint. Hacking a cloud provider’s hypervisor would give an attacker access to all of the customers using the service, Bob Hansmann, Forcepoint’s director of security technologies, told a Webinar last week. “They’re not targeting you, they may not even know you exist until they get into the infrastructure and get the data. Then they’re going to try to maximize the attack” by selling whatever data is gained. Also tempting attackers is the bandwidth cloud providers have, to possibly be leveraged for DDoS attacks. As attacks on cloud infrastructure increase it will be another reason why CISOs will be reluctant to put sensitive data in the cloud, he said, or to limit cloud use to processing but not storing sensitive data. CIOs/CISOs have to realize “the cloud is a lie,” he said. “There is no cloud. Any cloud services means data is going to someone’s server somewhere. So you need to know are they securing that equipment the same way you’re securing data in your organization … are the personnel vetted, what kind of digital defences do they have?” “You’re going to have to start pushing your cloud providers to meet compliance with the regulations you’re trying to be compliant with,” he added. That will be particularly important for organizations that do business in Europe with the coming into force next year of the European Union’s new General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) So answering questions such as now long does a cloud service hold the organization’s data, is it backed up securely, are employees vetted, is there third party certification of its use of encryption, how is it protected from DDoS attacks are more important than ever. Other predictions for next year include: –Don’t fear millennials. At present on average they are they second largest group (behind boomers) in most organizations. They do increase security risk because as a tech-savvy group they tend to over-share information – particularly through social media. So, Hansmann says, CISOs should use that to their advantage. “Challenge them to become security-savvy. Put in contests where employees submit they think are spam or phishing attacks, put in quarterly award recognitions, or something like that. Challenge them, and they will step up to the challnge. They take pride in their digital awareness.” Don’t try to make them feel what they do is wrong, but help them to become better. “They will be come a major force for change in the organiztion, and hopefully carry the rest of the organization with them.” –the so-called Digital Battlefield is the world. That means attackers can be nation-states as well as criminals. But CISOs should be careful what they do about it. Some infosec pros – and some politicians – advocate organizations and countries should be ready to launch attacks against a foe instead of being defensive. But, Forcepoint warns, pointing the finger is still difficult, with several hops between the victim and attacker. “The potential for mis-attribution and involving innocents is going to grow,” Hansmann said. “Nations are going to struggle with how do they ensure confidence in businesses, that they are a safe and secure place to do business with or through — and yet not over-react in a way that could cause collateral damage.” –Linked to this this the threat that will be posed in 2017 by automated attacks. The widespread weaponization of autonomous hacking machines by threat actors will emerge next year, Forcepoint says, creating an arms race to build autonomous patching. “Like nuclear weapons technology proliferation, weaponized autonomous hacking machines may greatly impact global stability by either preventing national defense protocols being engaged or by triggering them unnecessarily,” says the company. –Get ready for the Euopean GDPR. It will come into effect in May, 2018 and therefore next year will drive compliance and data protection efforts. “We’ve learned compliance takes a long time to do right, and to do it without disrupting your business.” Organizations may have to not only change systems but redefine processes, including training employees. CIOs need to tell business units, ‘We’re here to support you, but if you’re going to run operations through the EU this regulation is going to have impact. We need to understand it now because will require budgeting and changes to processes that IT doesn’t control,’ said Hansmann. –There will be a rise in what Forcepoint calls “corporate-incentivized insider abuse.’ That’s shorthand for ‘employees are going to cheat to meet sales goals.’ The result is staff falsifying reports or signing up customers signed up for services they didn’t order. Think of U.S. bank Wells Fargo being fined $185 million this year because more than 2 million bank accounts or credit cards were opened or applied for without customers’ knowledge or permission between May 2011 and July 2015. Over 5,000 staff were fired over the incidents. If organizations don’t get on top of this problem governments will regulate, Hansmann warned. Source: http://www.itworldcanada.com/article/cloud-infrastructure-attacks-to-increase-in-2017-predicts-forcepoint/389001
Read More:
Cloud infrastructure attacks to increase in 2017, predicts Forcepoint


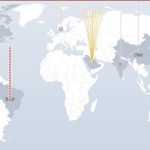 Experts believe that the electronic assault on the census site was a DDoS attack – a kind of electronic army that attacks an enemy’s website on every flank using millions of computers as soldiers. About 2000 of these attacks occur every day across the world, said DigitalAttackMap, a website that monitors such attacks. Only days ago, this type of attack shut down US Olympic swimming Michael Phelps’ commercial website, SCMagazine , which specialises in IT security, said. It said the attack happened fresh after Phelps’ gold medal-winning performance in the men’s 4×100 metre freestyle relay at the Rio Games. One hacking expert told Time magazine that any celebrity or high-profile site should expect these attacks. “Each celebrity on our target list will be either hacked or DDoSed,” a representative of hacking group New World Hackers said. Xbox, US Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump and the BBC have been among New World Hackers’ recent targets. DigitalAttackMap, a joint venture between Google Ideas and network security firm Arbor Networks, said these attacks had hit online gaming sites, newspapers and banks; Greek banks were crippled this year. Yet its site doesn’t show a DDoS attack on the ABS census site on Tuesday, bolstering claims by some that the attack didn’t take place. The DigitalAttackMap tracks DDoS attacks on a daily basis. The red flare over Brazil shows a serious DDoS attack. Photo: DigitalAttackMap.com The Australian Bureau of Statistics said its census site was hit four times by denial of service (DoS) attacks. A DoS is a broad term for attacks that attempt to crash an online system so that users cannot access it. Some IT and cybersecurity professionals speculated that a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack was to blame. A DDoS is a type of DoS attack in which hackers attempt to crash a system by flooding it with bots – or Trojan – accounts. DigitalAttackMap said attackers cripple websites, such as the ABS’ census site, by building networks of infected computers, known as botnets, by spreading malicious software through emails, websites and social media. Once infected, these machines can be controlled remotely, without their owners’ knowledge, and used like an army to launch an attack against any target. Some botnets are millions of machines strong. DigitalAttackMap says these botnets can generate huge floods of traffic to overwhelm a target. “These floods can be generated in multiple ways, such as sending more connection requests than a server can handle, or having computers send the victim huge amounts of random data to use up the target’s bandwidth. Some attacks are so big they can max out a country’s international cable capacity.” Adding to many people’s fears about the security of the census website before the attack, the information gained from these sites during an attack is sold on online marketplaces that specialise in information gained from these DDoS attacks, DigitalAttackMap said. “Using these underground markets, anyone can pay a nominal fee to silence websites they disagree with or disrupt an organisation’s online operations. A week-long DDoS attack, capable of taking a small organisation offline, can cost as little as $150,” the website said. Source: http://www.smh.com.au/technology/technology-news/what-are-the-dos-and-ddos-attacks-that-brought-down-the-census-20160809-gqowwp.html
Experts believe that the electronic assault on the census site was a DDoS attack – a kind of electronic army that attacks an enemy’s website on every flank using millions of computers as soldiers. About 2000 of these attacks occur every day across the world, said DigitalAttackMap, a website that monitors such attacks. Only days ago, this type of attack shut down US Olympic swimming Michael Phelps’ commercial website, SCMagazine , which specialises in IT security, said. It said the attack happened fresh after Phelps’ gold medal-winning performance in the men’s 4×100 metre freestyle relay at the Rio Games. One hacking expert told Time magazine that any celebrity or high-profile site should expect these attacks. “Each celebrity on our target list will be either hacked or DDoSed,” a representative of hacking group New World Hackers said. Xbox, US Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump and the BBC have been among New World Hackers’ recent targets. DigitalAttackMap, a joint venture between Google Ideas and network security firm Arbor Networks, said these attacks had hit online gaming sites, newspapers and banks; Greek banks were crippled this year. Yet its site doesn’t show a DDoS attack on the ABS census site on Tuesday, bolstering claims by some that the attack didn’t take place. The DigitalAttackMap tracks DDoS attacks on a daily basis. The red flare over Brazil shows a serious DDoS attack. Photo: DigitalAttackMap.com The Australian Bureau of Statistics said its census site was hit four times by denial of service (DoS) attacks. A DoS is a broad term for attacks that attempt to crash an online system so that users cannot access it. Some IT and cybersecurity professionals speculated that a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack was to blame. A DDoS is a type of DoS attack in which hackers attempt to crash a system by flooding it with bots – or Trojan – accounts. DigitalAttackMap said attackers cripple websites, such as the ABS’ census site, by building networks of infected computers, known as botnets, by spreading malicious software through emails, websites and social media. Once infected, these machines can be controlled remotely, without their owners’ knowledge, and used like an army to launch an attack against any target. Some botnets are millions of machines strong. DigitalAttackMap says these botnets can generate huge floods of traffic to overwhelm a target. “These floods can be generated in multiple ways, such as sending more connection requests than a server can handle, or having computers send the victim huge amounts of random data to use up the target’s bandwidth. Some attacks are so big they can max out a country’s international cable capacity.” Adding to many people’s fears about the security of the census website before the attack, the information gained from these sites during an attack is sold on online marketplaces that specialise in information gained from these DDoS attacks, DigitalAttackMap said. “Using these underground markets, anyone can pay a nominal fee to silence websites they disagree with or disrupt an organisation’s online operations. A week-long DDoS attack, capable of taking a small organisation offline, can cost as little as $150,” the website said. Source: http://www.smh.com.au/technology/technology-news/what-are-the-dos-and-ddos-attacks-that-brought-down-the-census-20160809-gqowwp.html