The number of DDoS (distributed denial-of-service) attacks that target weak spots in Web applications in addition to network services has risen during the past year and attackers are using increasingly sophisticated methods to bypass defenses, according to DDoS mitigation experts. Researchers from Incapsula, a company that provides website security and DDoS protection services, recently mitigated a highly adaptive DDoS attack against one of its customers that went on for weeks and combined network-layer with application-layer—Layer 7—attack techniques. The target was a popular trading site that belongs to a prominent player in a highly competitive online industry and it was one of the most complex DDoS attacks Incapsula has ever had to deal with, the company’s researchers said in a blog post. The attack started soon after an ex-partner left the targeted company and the attackers appeared to have intimate knowledge of the weak spots in the target’s infrastructure, suggesting that the two events might be connected, the researchers said. The attack began with volumetric SYN floods designed to consume the target’s bandwidth. It then progressed with HTTP floods against resource intensive pages, against special AJAX objects that supported some of the site’s functions and against Incapsula’s own resources. The attackers then switched to using DDoS bots capable of storing session cookies in an attempt to bypass a mitigation technique that uses cookie tests to determine if requests come from real browsers. The ability to store cookies is usually a feature found in full-fledged browsers, not DDoS tools. As Incapsula kept blocking the different attack methods, the attackers kept adapting and eventually they started flooding the website with requests sent by real browsers running on malware-infected computers. “It looked like an abnormally high spike in human traffic,” the Incapsula researchers said. “Still, even if the volumes and behavioral patterns were all wrong, every test we performed showed that these were real human visitors.” This real-browser attack was being launched from 20,000 computers infected with a variant of the PushDo malware, Incapsula later discovered. However, when the attack first started, the company had to temporarily use a last-resort mitigation technique that involved serving CAPTCHA challenges to users who matched a particular configuration. The company learned that a PushDo variant capable of opening hidden browser instances on infected computers was behind the attack after a bug in the malware caused the rogue browser windows to be displayed on some computers. This led to users noticing Incapsula’s block pages in those browsers and reaching out to the company with questions. “This is the first time we’ve seen this technique used in a DDoS attack,” said Marc Gaffan, co-founder of Incapsula. The challenge with application-layer attacks is to distinguish human traffic from bot traffic, so DDoS mitigation providers often use browser fingerprinting techniques like cookie tests and JavaScript tests to determine if requests actually come from real browsers. Launching DDoS attacks from hidden, but real browser instances running on infected computers makes this type of detection very hard. “We’ve been seeing more and more usage of application-layer attacks during the last year,” Gaffan said, adding that evasion techniques are also adopted rapidly. “There’s an ecosystem behind cybercrime tools and we predict that this method, which is new today, will become mainstream several months down the road,” he said. DDoS experts from Arbor Networks, another DDoS mitigation vendor, agree that there has been a rise in both the number and sophistication of Layer 7 attacks. There have been some papers released this year about advanced Layer 7 attack techniques that can bypass DDoS mitigation capabilities and the bad guys are now catching on to them, said Marc Eisenbarth, manager of research for Arbor’s Security Engineering and Response Team. There’s general chatter among attackers about bypassing detection and they’re doing this by using headless browsers—browser toolkits that don’t have a user interface—or by opening hidden browser instances, Eisenbarth said. In addition, all malware that has man-in-the-browser functionality and is capable of injecting requests into existing browsing sessions can also be used for DDoS, he said. Layer 7 attacks have become more targeted in nature with attackers routinely performing reconnaissance to find the weak spots in the applications they plan to attack. These weak spots can be resource-intensive libraries or scripts that result in a lot of database queries. This behavior was observed during the attacks against U.S. banking websites a year ago when attackers decided to target the log-in services of those websites because they realized they could cause significant problems if users are prevented from logging in, Eisenbarth said. “We continued to see attackers launch those type of attacks and perform reconnaissance to find URLs that, when requested, may result in a lot of resource activity on the back end,” he said. More and more companies are putting together DDoS protection strategies, but they are more focused on network-layer attacks, Gaffan said. They look at things like redundancy or how much traffic their DDoS mitigation solution can take, but they should also consider whether they can resist application-layer attacks because these can be harder to defend against than volumetric attacks, he said. With application-layer attacks there’s an ongoing race between the bad guys coming up with evasion techniques and DDoS mitigation vendors or the targeted companies coming up with remedies until the next round, Gaffan said. Because of that, both companies and DDoS mitigation providers need to have a very dynamic strategy in place, he said. “I think we will continue to see an evolution in the sophistication of application-layer attacks and we will see more and more of them,” Gaffan said. They won’t replace network-layer attacks, but will be used in combination with them, he said. Having Layer 7 visibility is very important and companies should consider technologies that can provide that, Eisenbarth said. In addition to that, they should perform security audits and performance tests for their Web applications to see what kind of damage an attacker could do to them, he said. Source: http://www.pcworld.com/article/2056805/applicationlayer-ddos-attacks-are-becoming-increasingly-sophisticated.html
Link:
Application-layer DDoS attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated


 Anonymous hackers, more precisely the ones who hacked a couple of Syrian government websites last week, have announced the start of a new campaign called Operation Throwback. ~ SoftPedia The goal of the operation is “to strike back against the oppressors of our freedom.” The hackers say they will launch distributed denial-of-service (DDOS) attacks against several high-profile websites. Today, on October 28, they plan on launching a cyberattack against the main website of T-Mobile. On October 31, they plan on attacking the website of the FBI, the NSA, Verizon, Microsoft and AT&T. The hacktivists urge their supporters to download DDOS tools and VPNs. The initiators of the operation are providing download links and instructions on how to use them. Earlier today, the hackers tested their “firepower” against the official website of the American Nazi Party. At the time of publishing NCB Interpol web site was down, apparantly from Ddos attack. Source: http://revolution-news.com/opthrowback-anonymous-to-launch-ddos-attacks-against-fbi-nsa/
Anonymous hackers, more precisely the ones who hacked a couple of Syrian government websites last week, have announced the start of a new campaign called Operation Throwback. ~ SoftPedia The goal of the operation is “to strike back against the oppressors of our freedom.” The hackers say they will launch distributed denial-of-service (DDOS) attacks against several high-profile websites. Today, on October 28, they plan on launching a cyberattack against the main website of T-Mobile. On October 31, they plan on attacking the website of the FBI, the NSA, Verizon, Microsoft and AT&T. The hacktivists urge their supporters to download DDOS tools and VPNs. The initiators of the operation are providing download links and instructions on how to use them. Earlier today, the hackers tested their “firepower” against the official website of the American Nazi Party. At the time of publishing NCB Interpol web site was down, apparantly from Ddos attack. Source: http://revolution-news.com/opthrowback-anonymous-to-launch-ddos-attacks-against-fbi-nsa/ 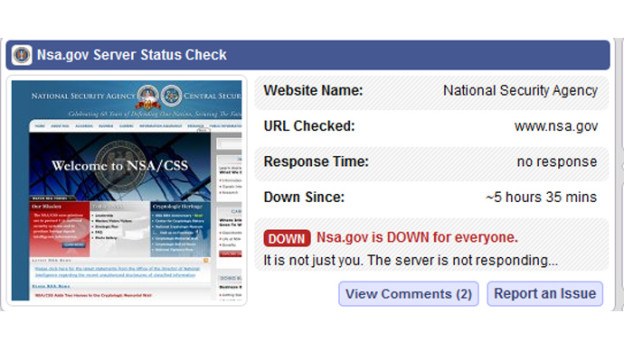
 The website for the United States National Security Agency suddenly went offline Friday. NSA.gov has been unavailable globally as of late Friday afternoon, and Twitter accounts belonging to people loosely affiliated with the Anonymous hacktivism movement have suggested they are responsible. Twitter users @AnonymousOwn3r and @TruthIzSexy both were quick to comment on the matter, and implied that a distributed denial-of-service attack, or DDoS, may have been waged as an act of protest against the NSA Allegations that those users participated in the DDoS — a method of over-loading a website with too much traffic — are currently unverified, and @AnonymousOwn3r has previously taken credit for downing websites in a similar fashion, although those claims have been largely contested. The crippling of NSA.gov comes amid a series of damning national security documents that have been disclosed without authorization by former intelligence contractor Edward Snowden. The revelations in the leaked documents have impassioned people around the globe outraged by evidence of widespread surveillance operated by the NSA, and a massive “Stop Watching Us” rally is scheduled for Saturday in Washington, DC. DDoS attacks are illegal in the United States under the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act, or CFAA, and two cases are currently underway in California and Virginia in which federal judges are weighing in on instances in which members of Anonymous allegedly used the technique to take down an array of sites during anti-copyright campaigns waged by the group in 2010 and 2011. In those cases, so-called hacktivsits are reported to have conspired together to send immense loads of traffic to targeted websites, rendering them inaccessible due to the overload.
The website for the United States National Security Agency suddenly went offline Friday. NSA.gov has been unavailable globally as of late Friday afternoon, and Twitter accounts belonging to people loosely affiliated with the Anonymous hacktivism movement have suggested they are responsible. Twitter users @AnonymousOwn3r and @TruthIzSexy both were quick to comment on the matter, and implied that a distributed denial-of-service attack, or DDoS, may have been waged as an act of protest against the NSA Allegations that those users participated in the DDoS — a method of over-loading a website with too much traffic — are currently unverified, and @AnonymousOwn3r has previously taken credit for downing websites in a similar fashion, although those claims have been largely contested. The crippling of NSA.gov comes amid a series of damning national security documents that have been disclosed without authorization by former intelligence contractor Edward Snowden. The revelations in the leaked documents have impassioned people around the globe outraged by evidence of widespread surveillance operated by the NSA, and a massive “Stop Watching Us” rally is scheduled for Saturday in Washington, DC. DDoS attacks are illegal in the United States under the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act, or CFAA, and two cases are currently underway in California and Virginia in which federal judges are weighing in on instances in which members of Anonymous allegedly used the technique to take down an array of sites during anti-copyright campaigns waged by the group in 2010 and 2011. In those cases, so-called hacktivsits are reported to have conspired together to send immense loads of traffic to targeted websites, rendering them inaccessible due to the overload.